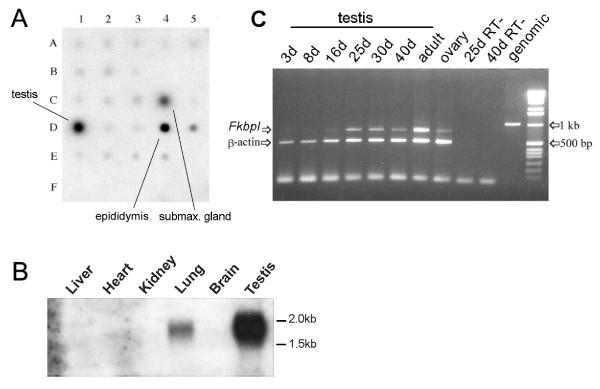
Figure 2.
Fkbpl transcription in mouse. A. A Multiple Tissue Array normalised polyA+ RNA blot was hybridised to a radiolabelled Fkbpl cDNA. The locations of testis, epididymis and submaxillary gland RNA are indicated. Top row: brain (A1), eye (A2), liver (A3), lung (A4), kidney (A5); Second row: heart (B1), skeletal muscle (B2), smooth muscle (B3), pancreas; Third row: (C1), thyroid (C2), thymus (C3), submaxillary gland (C4), spleen (C5); Fourth row: testis (D1), ovary (D2), prostate (D3), epididymus (D4), uterus (D5); Fifth row: embryo 7 days (E1), embryo 11 days (E2), embryo 15 days (E3) and embryo 17 days (E4); Last row: negative controls (F1-4). Positions not listed (e.g. B4) are blank. B. Northern blotting. Total RNA (20 ug) was extracted from the tissues indicated and fractionated on a 1% gel containing formamide before transferring to nitrocellulose and hybridising to the cDNA probe used in A. The positions of relevant size markers are indicated at right. The experiment was repeated twice. C. RT-PCR of total RNA isolated from testis at different days postnatally. The primers span the intron, allowing any contaminating genomic product to be easily distinguished (right); β-actin is used as an internal positive control: RT- are negative controls. The experiment was repeated twice.