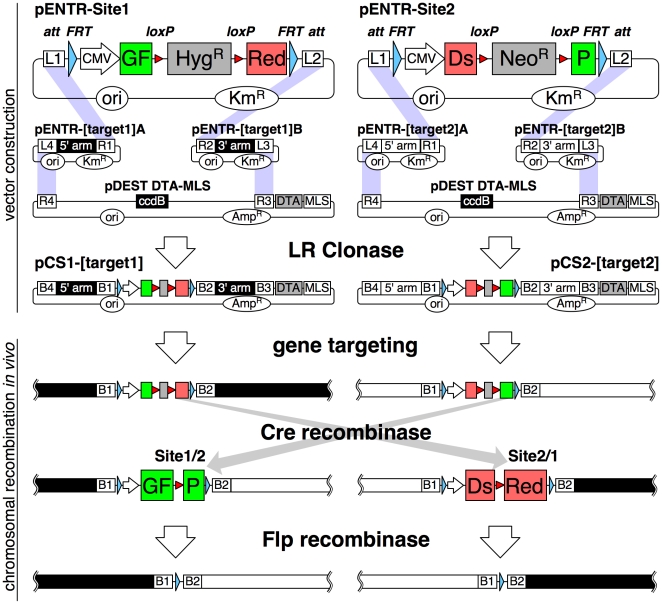
Figure 1. Scheme for vector construction and chromosomal recombination.
(upper) pENTR-Site1 plasmid contains cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter-driven fusion gene, the first half consisting of GFP (green box) and the last half of dimer2 (a DsRed variant, red box) with an intervening hygromycin-resistance gene (grey box) flanked by loxP sites (red triangles), outer two FRT sites (blue triangles) and attL1 and attL2 sites (open box). pENTR-Site2 expresses a fusion gene complementary to pENTR-Site1 harboring a neomycin-resistance gene (grey box). These vectors in addition to 5′- and 3′-targeting homology arm vectors and the pDEST DTA-MLS destination vector were assembled into targeting vectors by LR Clonase. Purple shadows connect att sites to be recombined. (lower) After gene targeting into homologous chromosomal regions, Cre first removes drug-resistance genes and then recombines distant loxP sites. After recombination, GFP and dimer2 mRNAs are spliced and expressed. Expression of Flp excises fluorescent protein genes to achieve clean rearrangement, leaving a 103-bp element. DTA, diphtheria toxin A; MLS, multiple linearization sites (PmeI, AscI, I-SceI, SwaI, PacI); ori, replication origin; KmR, kanamycin-resistance gene; AmpR, ampicillin-resistance gene; ccdB, bacterial ccdB gene.