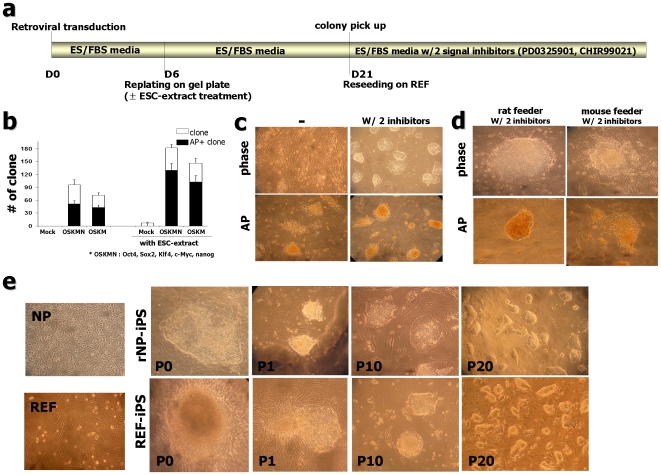
Figure 1. Generation of iPS cells from rat neural precursor cells (rNP) and embryonic fibroblast cells (REF).
(a) Schematic time schedule of rat-iPS generation. (b) Clone formation after pluripotent factors induction with or without ESC-extract treatment. Shown are alkaline phosphatase (AP)-positive clone numbers (black columns) from the total numbers of colony (white columns) at 20 days after transduction. (Each column from n = 14 of 6 independent experiments, error bars indicate S.E.; *OSKMN: Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc, Nanog) (c) Colonies with ESC morphology could be maintained in the presence of MEK inhibitor, PD0325901 (0.5 µM) and GSK3β inhibitor, CHIR99021 (3 µM) (right). Colonies under conventional ES culture condition lost AP-positive character and kept differentiating (left). (d) Rat embryonic fibroblast (REF)-derived feeders are necessary for maintaining ESC-like character. After several passages, ESC-like colonies lost AP activity on mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF)-derived feeders combined with 2 inhibitors, PD0325901 and CHIR99021. (e) Phase-contrast micrograph of rat embryonic NP and fibroblast (far left). Isolation of rNP-iPS and REF-iPS cells based on morphology, pictures on the right show rNP-iPS #2 clone and REF-iPS #3 formation, respectively. P0 image shows the representative clone formed at 20 days after infection (P0: passage 0) and image P1 was taken at 7 days after picking (passage 1). Examples of homogeneous colonies from images on the left at passage number 10 (P10) and on the right at passage number 20 (P20).