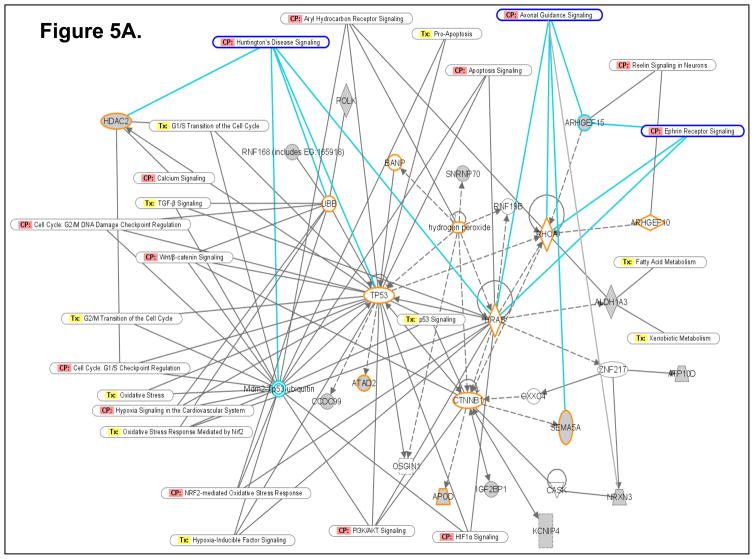
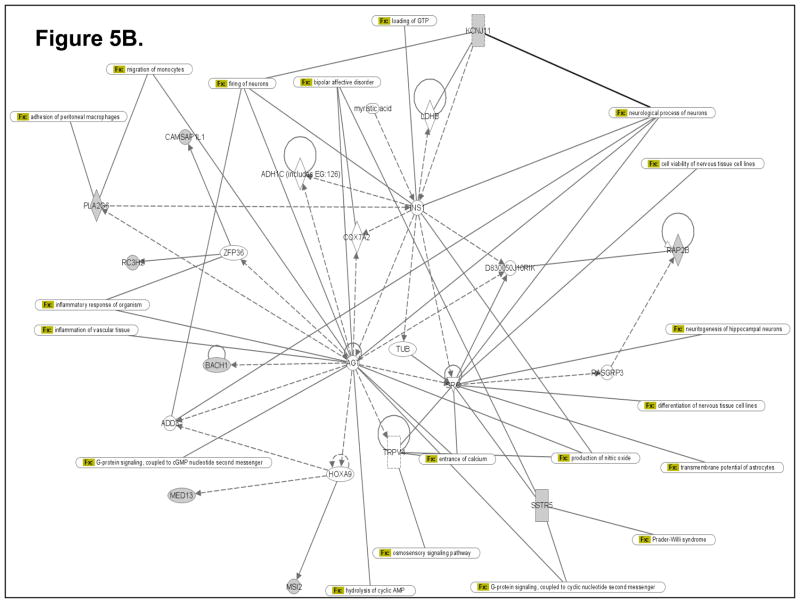
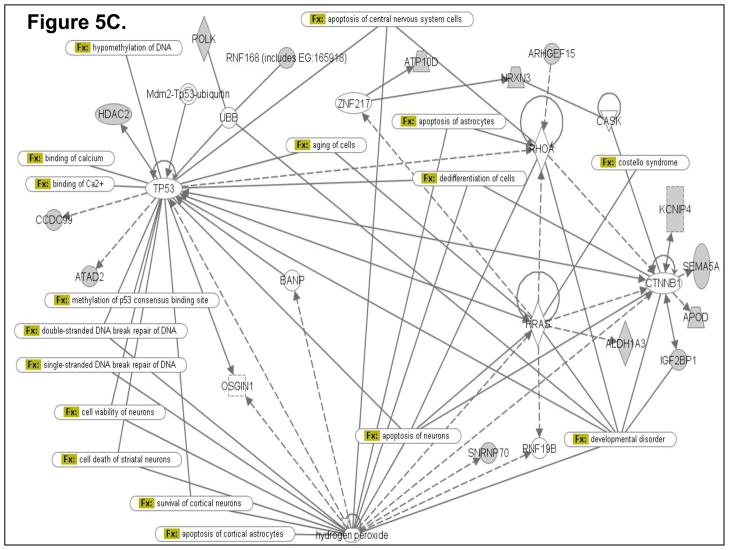
Figure 5.
Computational gene interaction predictions: selected gene networks (A, B, C) in the fetal hippocampus following ETS exposure. Gene networks were constructed with Ingenuity Systems Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Several differentially regulated genes from the study were used to construct gene association maps for predicting effects of prenatal exposure to ETS on various cellular and molecular events in the developing mouse hippocampus. The first statistically significant network (Fig. 5A) that was generated, includes p53 tumor suppressor (TP53), Hras oncogene, β-catenin (CTNNB1) and Ubiquitin-B (UBB), and also consists of several genes such as those encoding HDAC2, Semaphorin-5A, Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 (ALDH1A3), Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 15 (ARHGEF15), Apolipoprotein D, Polymerase kappa, and Neurexin-3 (NRXN3) among others, which demonstrated significant differential expression within the hippocampus as a consequence of prenatal ETS exposure (Table 3). The second statistically significant network (Fig. 5B) consists of – Rous sarcoma oncogene (SRC), Angiotensinogen (AGT), Zinc finger protein 36 (ZFP36) and Hoxa9, in addition to a number of genes encoding proteins such as Somatostatin receptor 5 (SSTR5), Potassium inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11 (KCNJ11), Musashi-2 (MSI2), and Phospholipase A2, group VI (PLA2G6) among others, which are either up- or down-regulated in the developing hippocampus exposed to in utero sidestream tobacco smoke (Table 3). The third statistically significant network (Fig. 5C) is composed of – p53, RhoA, β-catenin, Hras, as well as several differentially expressed genes – detected in the present study – such as those encoding – Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (Igf2bp1), HDAC2, Apolipoprotein D (APOD), ATPase Class V, type 10D (ATP10D), Ring finger protein (RNF168), ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 (ATAD2), etc. (Table 3). Solid lines specify direct relationships whereas dotted lines indicate indirect interactions.