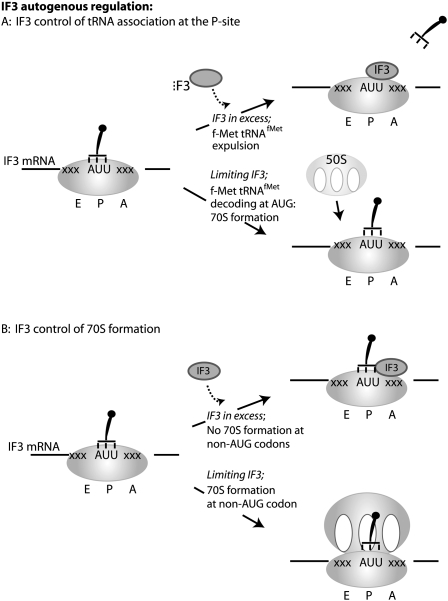
FIGURE 2.
Translation of IF3 is autogenously controlled via a negative feedback loop acting at the level of initiation codon detection. (A) In vitro evidence suggests IF3 catalyzes continuous eviction of tRNA from the ribosomal P-site (Antoun et al. 2006). This ejection mechanism is faster if the initiator tRNA is noncognate for the initiation codon being used. For this reason, in the presence of IF3, initiation on the IF3 mRNA is highly inefficient due to the use of an AUU initiation codon. In the absence of IF3, initiator tRNA is not ejected, and IF3 translation is begun. (B) Some studies indicate a model where IF3 selectively prevents 70S formation if a noncognate P-site interaction is encountered (Grigoriadou et al. 2007). In the absence of IF3, 70S formation is not sensitive to initiator tRNA decoding fidelity, thus initiation at the infC (IF3) AUU codon is permitted.