Figure 2 (a-e).
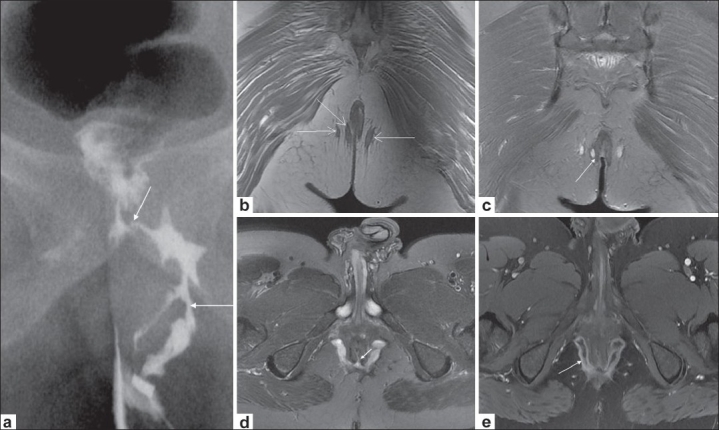
Crohn's disease with extrasphincteric fistulae. Conventional fistulogram (a) shows a branching left perianal fistula (long arrow), communicating with the rectum (short arrow). Coronal T1W image (b) depicts bilateral ischiorectal tracts (arrows). Coronal fat-saturated T2W image (c) depicts one transsphincteric tract interrupting the right external sphincter (arrow), the two other tracts being extrasphincteric. Axial fat-saturated T2W image (d) shows bilateral ischiorectal abscesses communicating across the midline with a posterior internal opening at 6 o'clock position (arrow). Axial postcontrast T1W image (e) depicts enhancement of the horseshoe abscess (arrow)
