Figure 4 (a-d).
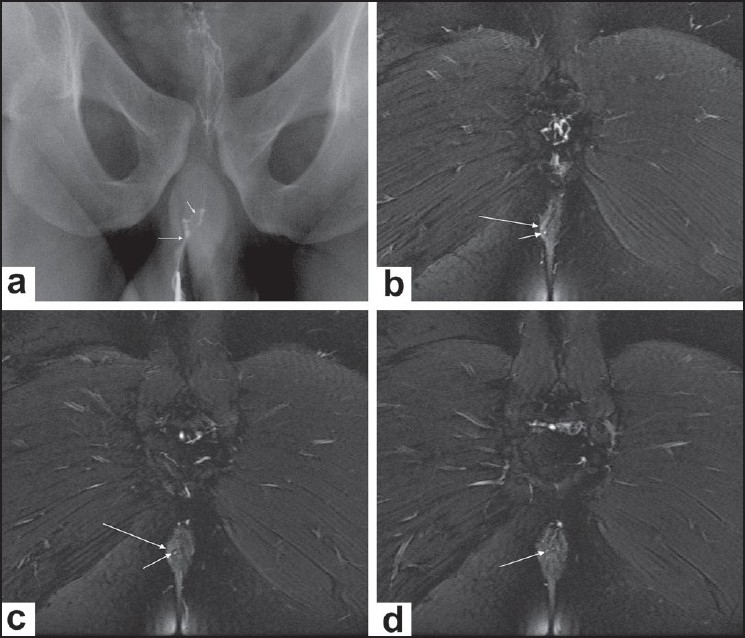
Intersphincteric fistula. Conventional fistulogram (a) delineates a thin tract lying (long arrow) close to the midline, with internal communication (short arrow). Sequential posterior to anterior coronal fat-saturated T2W images (b-d) reveal a small hyperintense tract (short arrow in b,c) lying entirely medial to the right external sphincter (long arrow in b, c) and opening within the anal canal (arrow in d)
