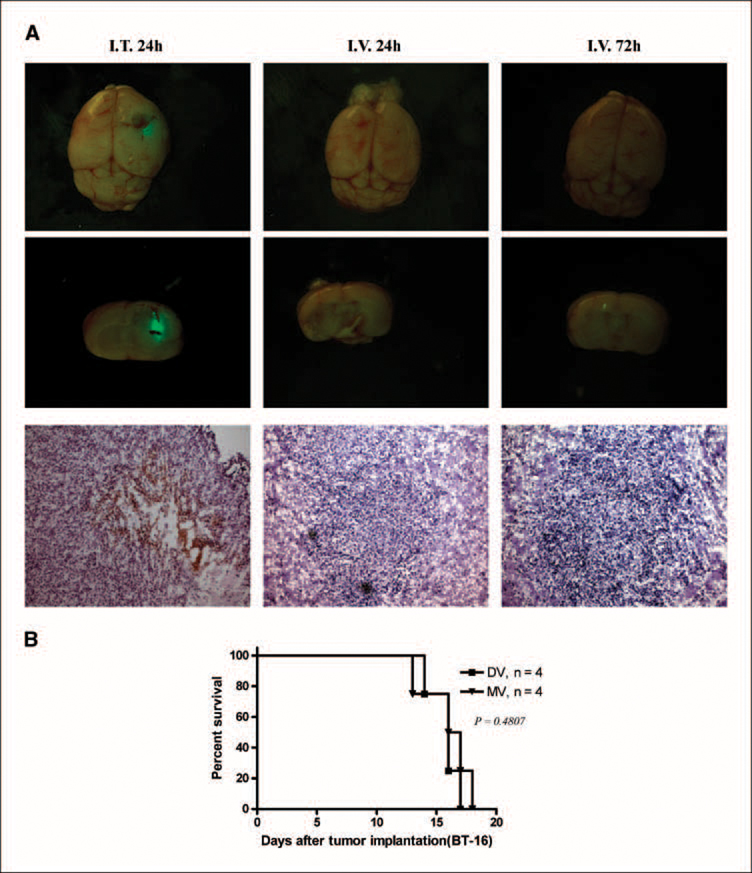
Fig. 4.
Distribution and survival of i.v. administered MV in nude mice bearing BT-16 rhabdoid tumors. A, nude mice bearing BT-16 intracranial tumors were treated with MV (i.v.) at a dose of 5 × 107 pfu/mouse (the highest dose of virus available) 10 d after tumor cell implantation. Animals were sacrificed at different time points (24 h, 72 h) after virus infection. Top and middle lane, photomicrograph of GFP-labeled virus present in the rhabdoid tumor (n = 3 mice per group; magnification, × 20). Arrows, GFP virus expression. Bottom row, immunohistochemical staining for MT-7 protein (arrow, brown staining; magnification, ×100). Left column, MV i.t (5 × 106 pfu/mice) as a positive control. B, Kaplan-Meier showing the survival of BT-16 tumor-bearing mice after i.v. administration of PBS (DV, n = 4; MV, n = 4). All P values are two-sided. I.v. delivery of MV did not prolong survival (DV and MV, log-rank test, P = 0.4807).