Table 4.
Rotamer-dependent helical consensus sequence templates derived from the database and comparison to previous designed protein sequences.
| A. Optimal sequences by rotamer (Contact residues highlighted in grey) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ligand Histidine Rotamer | Sequence | |
| t73 | I XXX XXX XXH XXH XX XX I I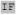
|
|
| m166 |
 XX XX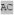 XA XA HXX HXX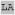
|
|
| t-86 | AHXX XX XX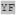
|
|
| m80 |
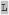 KX KX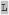 SX SX HXX HXX |
|
| B. The t73 sequence template compared to previous dihelical bis-histidine designs | ||
| Protein | Sequence | Reference |
| optimal t73 | I XXX XXX XXH XXH XX XX I I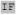
|
this work |
| HP-1 | EIWKQHEEALKKFEEALKQFEELKKL | (22) |
| ME1 | ILLASYGHRRLRKK | (9) |
| D2-heme | REKHRALAEQVYATGQMLKN | (8) |
| H2α17-FF | AEAFFKAHAEFFAKAA | (26) |
| Δ7-His | EIWKLHEEFIKLFEERIKKL | (25) |
| 6H7H | DKWKQHHQEFKQFLKELKQKLEEIA | (27) |
| AP1 | DPLVVAASIIGILHFIEWILDRGGNGEIFKQ | (18) |
| PAsc | QQKALQTAKEFQQAMQKHKQY | (34) |
| MOP-1 | NALELHEKALKQLEELLKKL | (35) |
| C. The m166 sequence template compared to the previous C-type cytochrome design | ||
| Protein | Sequence | Reference |
| optimal m166 |
 XX XX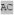 XA XA HXX HXX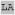
|
this work |
| cHH | ELLKLHEELLKKFEECLKLHEERLKKL | (10) |
