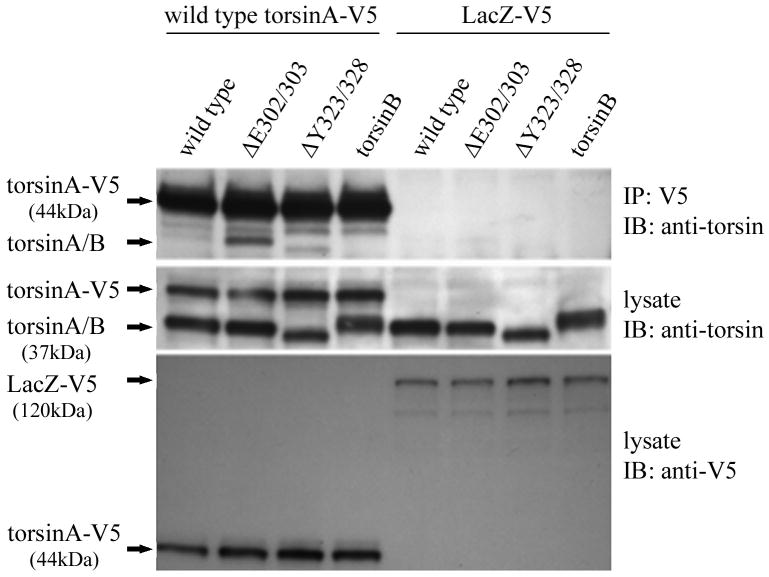
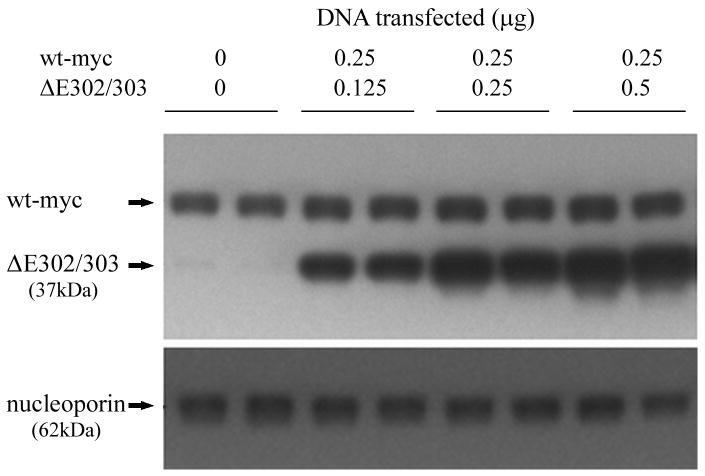
Figure 2.
Mutant torsinA interacts with wildtype torsinA in vivo. A. Self-interaction of torsinA was assessed by cotransfecting V5 tagged wildtype torsinA and various untagged torsin constructs into HEK293 cells. A construct encoding V5 tagged LacZ was used as a negative control. The upper panel shows the results of immunoprecipitation (IP) using monoclonal anti-V5 and the immunoblot (IB) probed with a polyclonal antibody that detects torsinA and torsinB (torsin290). The lower panels show the inputs (lysates, 10μg total protein per lane) probed with torsin and V5 antibodies respectively. The efficiency of the IP for the V5 tag is demonstrated by the presence of the Tor-V5 protein in the IP. B. Mutant torsinA does not alter wildtype torsinA steady-state protein levels. Cells were cotransfected with constant amounts of constructs encoding myc tagged wildtype torsinA (0.25μg plasmid per transfection) and increasing amounts of untagged mutant torsinA (0 to 0.5μg plasmid) in duplicate. Western blot analysis was performed with polyclonal anti-torsin antibody (torsin290) and monoclonal anti-nucleoporin to demonstrate equivalent loading of protein lysate.