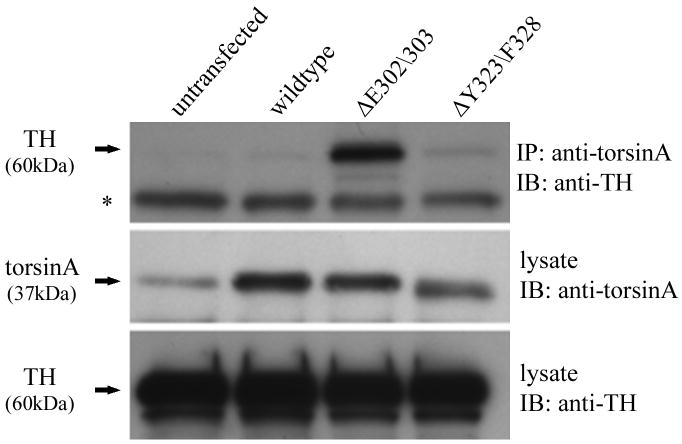
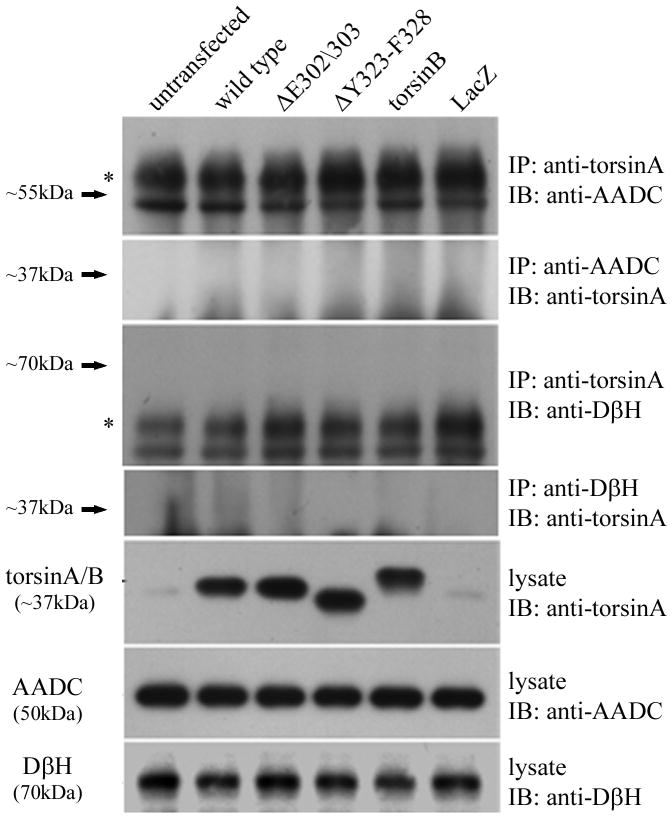
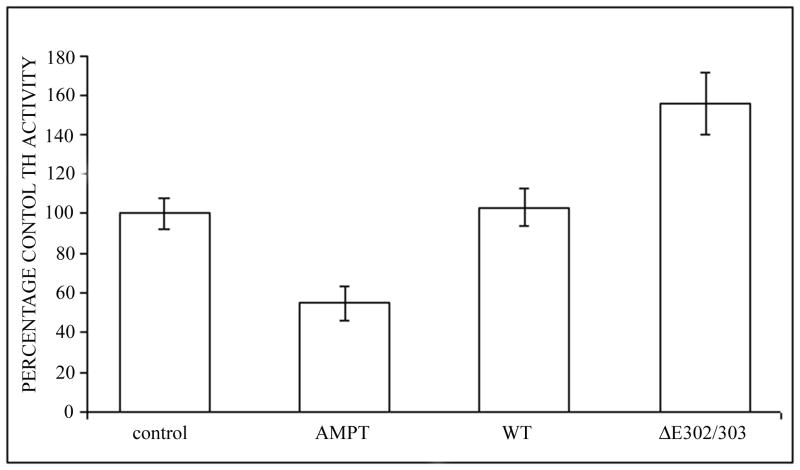
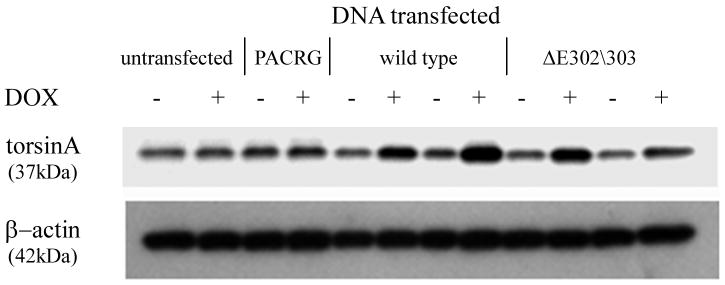
Figure 5.
TorsinA and TH interact in vivo and is enhanced by the ΔE302/303 mutation. A. The interaction between torsinA and TH was assessed by transfecting M17 neuroblastoma cells with constructs encoding wildtype or mutant torsinA. The upper panel shows the results of immunoprecipitation (IP) using a polyclonal antibody to torsin (torsin290) and the immunoblot (IB) probed with a monoclonal antibody that detects TH. The faint TH signal seen in the untransfected and wildtype lanes, indicating interaction of TH with wildtype torsinA, was greatly enhanced in the presence of ΔE302/303 mutant torsinA. The lower panels show the inputs (lysates, 10μg total protein per lane) probed with torsin and TH antibodies respectively. The * indicates the IgG heavy chain. B. TorsinA does not interact with other enzymes involved in dopamine synthesis. M17 neuroblastoma cells were transfected with various untagged torsin constructs. The upper four panels show the results of immunoprecipitation (IP) using a polyclonal antibody to torsinA (torsin290), AADC or DβH. Neither AADC nor DβH was observed to co-immunoprecipitate with any of the torsin proteins. The expected position of immunoprecipated protein is marked by the arrow. The * indicates the IgG heavy chain. The lower panels show the inputs (lysates, 10μg total protein per lane) probed with torsin, AADC and DβH antibodies respectively. C. Mutant torsinA affects TH activity. SY5Y cells were stably transfected with torsinA or an unrelated control protein (Parkin Co-Regulated Gene) under an inducible promoter system. Clonal cell lines (n>3 for each construct) were independently assayed a minimum of five times (mean±SEM). TH activity was assessed for both the non-induced and induced state and expressed as % change compared to the non-induced cells. A significant increase in fluorescence was observed in the cells expressing ΔE302/303 torsinA but not wildtype torsinA. One-way ANOVA confirmed a difference in TH activity between the three groups [F(2,16)=7.74, p=0.004] and tukey post-hoc comparison of the 3 groups indicated a significant increase in TH activity after induction of ΔE302/303 when compared to cell lines expressing wildtype torsinA (p=0.006). D. Inducible expression of torsinA. To confirm doxycycline-induced expression of wildtype and mutant torsinA, SY5Y cells cultured in the absence or presence of 0.1μg/mL doxycycline were analysed by western blot with an anti-torsinA antibody (torsin290). Equal loading (10μg total protein per lane) was confirmed by analysis using an anti-β actin antibody.