Figure 1.
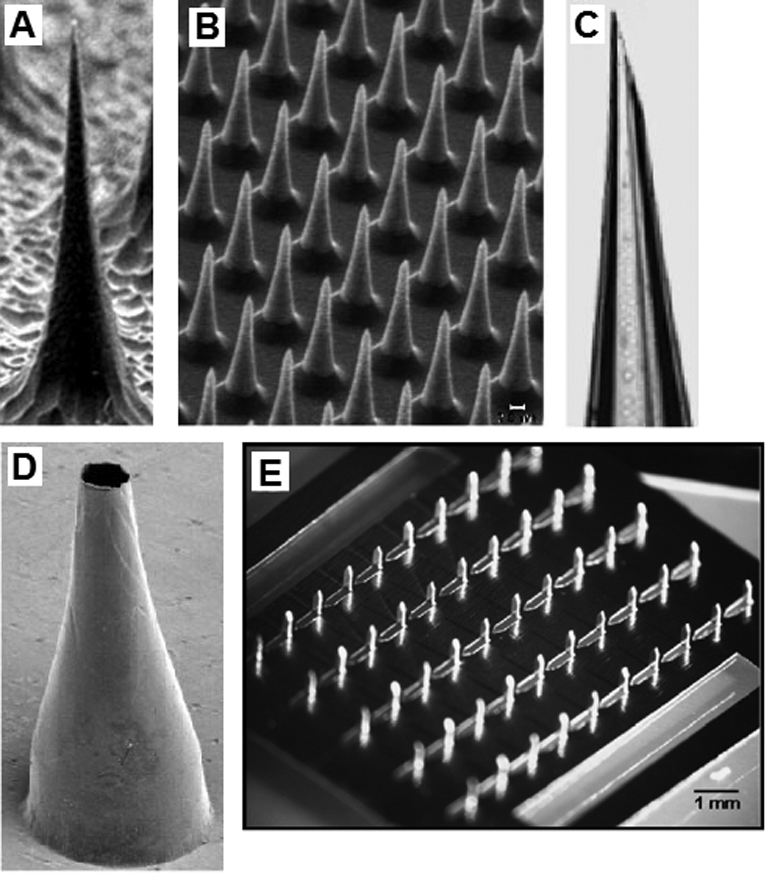
(a) Solid silicon microneedle fabricated by reactive ion etching. (b) Solid silicon microneedle array fabricated by reactive ion etching. (c) Hollow glass microneedle fabricated using a micropipette puller. (d) Hollow metal microneedle fabricated by electroplating a master structure. (e) Solid metal microneedles fabricated by laser machining and bending a metal sheet.
(a–d) Reprinted from the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies, D. V. McAllister, P. M. Wang, S. P. Davis, J. H. Park, P. J. Canatella, M. G. Allen, M. R. Prausnitz, Vol 100, 13755–13760, Copyright (2003) National Academy of Sciences, U. S. A.
(e) Reprinted from Journal of Controlled Release, Vol 117, H. S. Gill, M. R. Prausnitz, Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery, 227–237, Copyright (2007), with permission from Elsevier.
