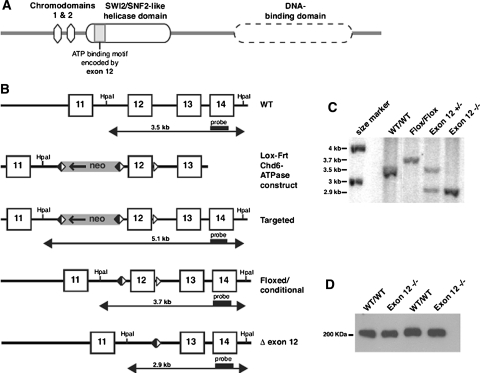
Fig. 1.
Generation of a Chd6 Exon 12 −/− mouse line. a Domain architecture of the Chd6 protein. The SWI2/SNF2 helicase domain contains seven conserved motifs, including motif I (ATP-binding region) and Ia (DNA binding), which are encoded by exon 12 of mChd6. b Gene targeting strategy: A portion of the mChd6 gene structure is shown, including exons 11-14 (boxes), and the HpaI restriction enzyme sites used for Southern blot analysis. The targeting vector “lox-frt-Chd6-ATPase” was designed to enable the deletion of mChd6 exon 12 by loxP site-specific recombination. The loxP sites (white triangles) and direction of transcription of the Neomycin-resistance gene (Neo) are indicated (arrow). The Frt-flanked Neo-cassette was removed by flp-mediated, site-specific recombination (Frt recombination elements are black triangles). The structure of the desired allele (Δ-exon 12) was obtained after Cre-mediated excision of the floxed exon 12. The Southern probe and the sizes of HpaI restriction fragments detected by this probe in wild-type (WT) and targeted DNA are shown. c Southern analysis of tail clip genomic DNA: The WT Chd6 allele (3.5 kb band) is distinguishable from the floxed conditional Chd6 allele (3.7 kb) and the Chd6 Exon 12 −/− allele (2.9 kb). d Western analysis: Detection of WT Chd6 (305 kDa) and mutant Δ479-558Chd6 (296 kDa) in lung extracts from WT and Chd6 Exon 12 −/− animals, respectively. The small difference in molecular weights between WT and mutant Chd6 could not be detected by this assay