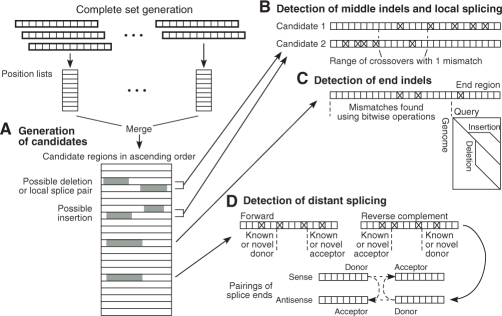
Fig. 5.
Efficient detection of indels and splice pairs. (A) The complete set method generates candidate regions with supporting 12mers (gray). (B) Pairs of candidates within the allowed distance are tested for middle indels and short-distance splice pairs. The constraint on number of mismatches (shown for the value 1) determines a range of crossover points. (C) End indels are tested in the distal 14 nt when the long region of the read has a sufficiently low number of mismatches. (D) Long-distance splicing is detected by identifying known or novel splice sites in single candidate regions within areas defined by constraints on number of mismatches. Candidate regions with donor and acceptor splice sites are then paired to reveal splice junctions.