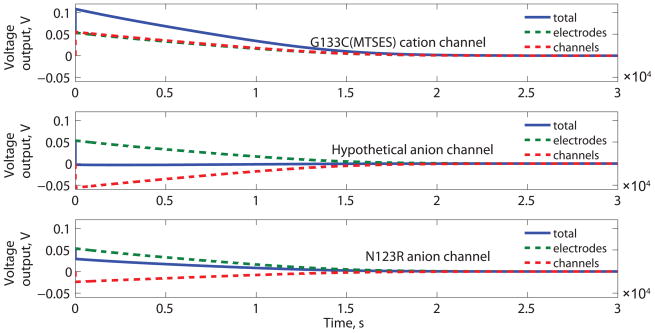
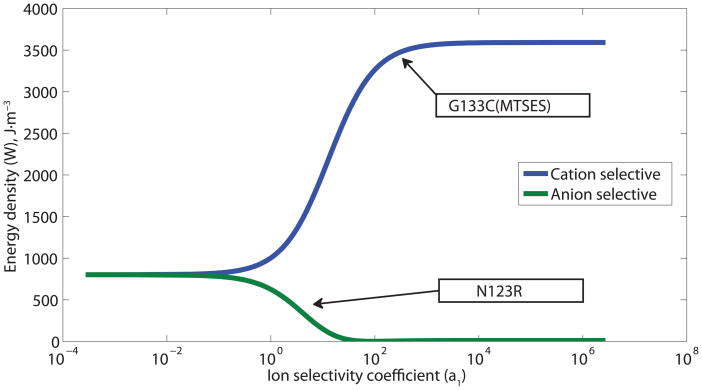
Figure 2.
Performance of a DC biobattery with cation and anion selective α-HL mutants. (A) The cation selective channel (MTSES G133C) uses parameters based on published MTSES treated G133C α-HL mutants. For comparison, calculations using two anion-selective channels are shown: a hypothetical anion selective channel that is as strongly anion specific as the MTSES G133C is cation specific and parameters based on published N123R channels[42]. For each case, the total potential (Et) is shown along with the contributions due to the channels (Er) and the electrodes (Ec). (B) The output energy density (W) as a function of ion selectivity (a1) of the membrane proteins for both cation and anion specific channels. The selectivity reported for specific mutants, MTSES treated G133C and N123R, is highlighted with arrows.