Abstract
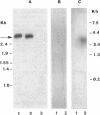
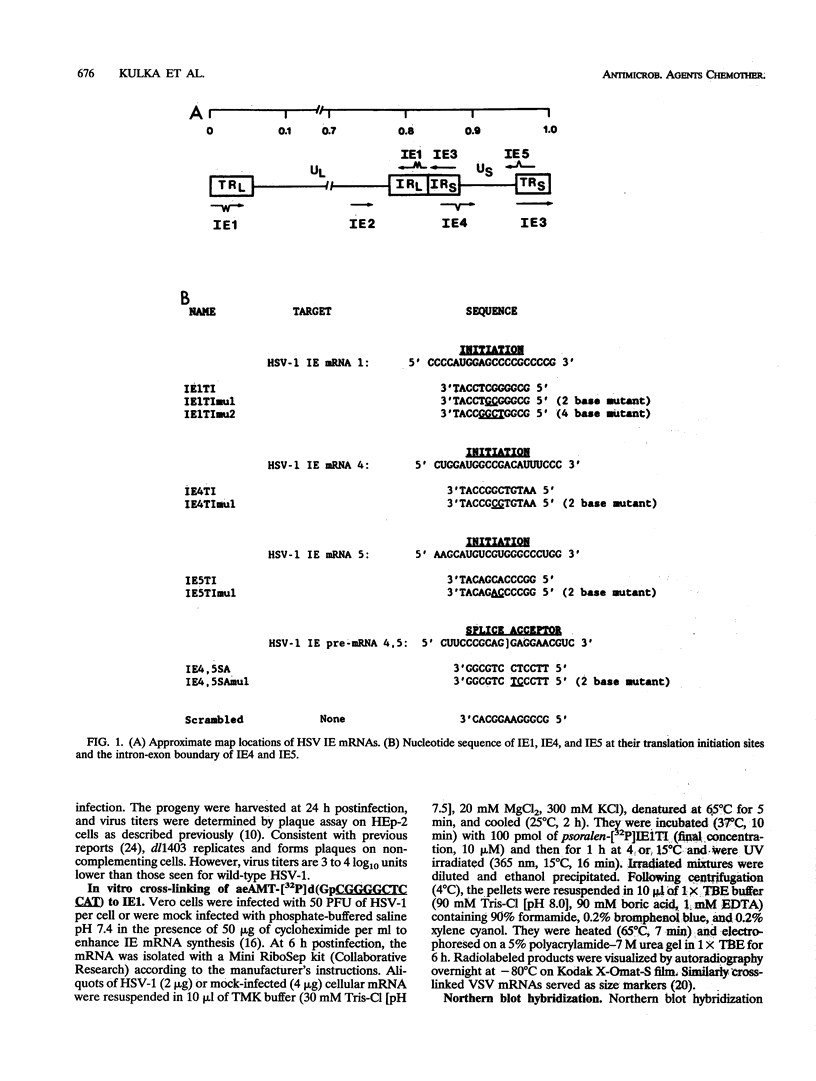
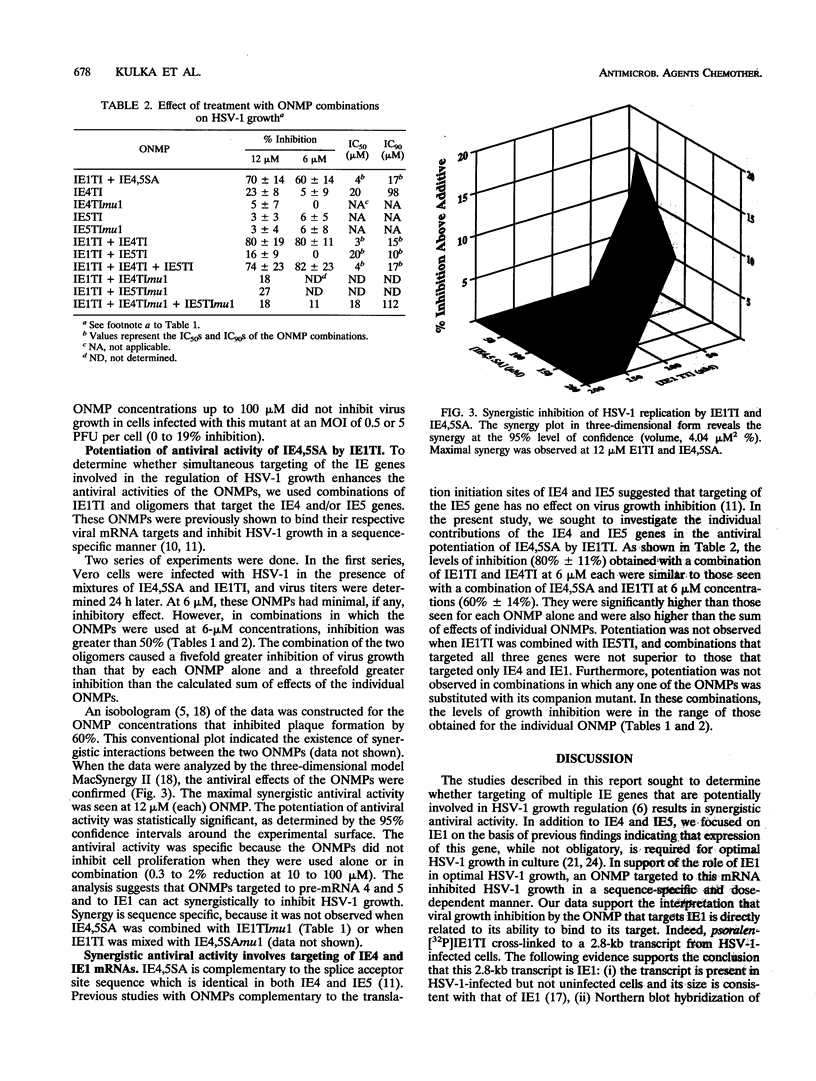
An oligonucleoside methylphosphonate (ONMP) complementary to the splice acceptor site of immediate-early (IE) pre-mRNAs 4 and 5 (IE4,5SA) inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) growth in vitro and in infected animals. The antiviral effect appears to be due to inhibition of IE pre-mRNA 4 and 5 splicing and/or IE4 gene expression (M. Kulka, M. Wachsman, S. Miura, R. Fishelevich, P. S. Miller, P. O. P. Ts'o, and L. Aurelian, Antiviral Res. 20:115-130, 1993). We describe the potentiation of antiviral activity when we targeted two IE genes with different ONMPs. A psoralen derivative of an ONMP complementary to the IE mRNA 1 (IE1) translation initiation site (IE1TI) covalently bound a 2.8-kb transcript that hybridized with a 20-base oligonucleotide complementary to the 5' leader sequence of IE1 but not a 20-base oligonucleotide complementary to the first intron of IE1. IE1TI inhibited IE1 gene expression and virus replication in cells infected with HSV-1 in vitro. Inhibition was specific because it was not observed with oligomers mutated in two (IE1TImu1) or four (IE1TImu2) central residues or in cells infected with an IE1 deletion mutant (HSV-1 dl1403). IE1TI potentiated the antiviral activity of IE4,5SA (synergistic effect), while potentiation was not observed when IE4,5SA was mixed with IE1TImu1. A similar synergistic effect was seen when IE1TI was mixed with an ONMP complementary to the translation initiation site of IE mRNA 4 but not with an ONMP complementary to the translation initiation site of IE mRNA 5. These findings suggest that synergistic antiviral activity is mediated by targeting at least two IE genes (IE1 and IE4).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris C. H., Blake K. R., Miller P. S., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus protein synthesis and infection by sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6268–6275. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan P., Miller P. S. Photo-cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to single-stranded DNA. Bioconjug Chem. 1990 Jan-Feb;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1021/bc00001a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake K. R., Murakami A., Spitz S. A., Glave S. A., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O., Miller P. S. Hybridization arrest of globin synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates and cells by oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6139–6145. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The regulation of transcription of viral and cellular genes by herpesvirus immediate-early gene products (review). Anticancer Res. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4A):589–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. Antisense RNA: its functions and applications in gene regulation--a review. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemont B., Verrier B., Epstein A. L., Machuca I. Expression of immediate-early genes in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected XC cells: lack of ICP22 (68K) polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1331–1340. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Cushman C. D., Miller P. S. Photochemical cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to rabbit globin messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9113–9121. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka M., Wachsman M., Miura S., Fishelevich R., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O., Aurelian L. Antiviral effect of oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonates) complementary to the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNAs 4 and 5. Antiviral Res. 1993 Feb;20(2):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(93)90002-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Ackermann M., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a viable herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant lacking coding sequences of the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.807-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., McParland K. B., Jayaraman K., Ts'o P. O. Biochemical and biological effects of nonionic nucleic acid methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1874–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard M. N., Prichard L. E., Shipman C., Jr Inhibitors of thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase potentiate the antiviral effect of acyclovir. Antiviral Res. 1993 Mar;20(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(93)90024-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Ogle W. O., Roizman B. Processing of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein alpha 22 mediated by the UL13 protein kinase determines the accumulation of a subset of alpha and gamma mRNAs and proteins in infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Halliburton I. W., Meignier B., Silver S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 mutant deleted in the alpha 22 gene: growth and gene expression in permissive and restrictive cells and establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.338-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]