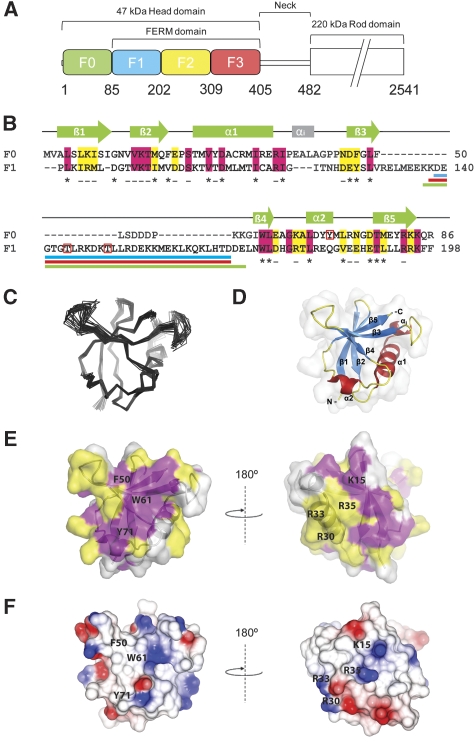
Figure 1.
Solution structure of the N-terminal F0 domain of talin1. (A) Domain structure of the talin1 head; residue numbers indicate domain boundaries. (B) Amino-acid sequence alignment and secondary structure of the F0 and F1 domains. Invariant residues are in magenta and conserved residues in yellow. Buried residues are marked ‘–' (<80% exposed) and ‘*' (<20% exposed). Phosphorylation sites are indicated by red boxes. Loop deletion regions are shown by coloured lines under the sequence; Δ30 (blue), Δ31 (red) and Δ34 (green). (C, D) Solution structure of the F0 domain; (C) superposition of the 20 lowest energy structures. (D) Ribbon diagram of the F0 structure. (E, F) Surface representations of the talin1 F0 domain. (E) Surface representation showing the position of residues conserved among talins. The sequences used in the conservation analysis are shown in Supplementary Figure 2A, colour scheme as in (B). A conserved surface comprising helix 1 and the loop between helix 1 and strand 3 (shown in the right panel) is present in all talin isoforms. (F) Electrostatic surface of talin1 F0. Residues discussed in the text are marked.