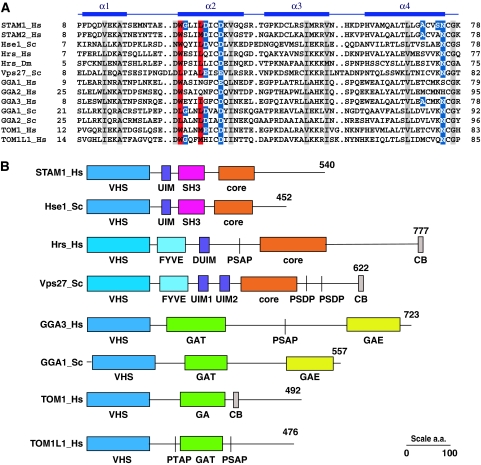
Figure 2.
The structural ubiquitin (Ub)-binding motif is conserved in nearly all VHS (Vps27, Hrs, and STAM) domains. (A) Aligned sequences of VHS domain-containing proteins in the region corresponding to the N-terminal half of the domain. The secondary structure of the human STAM1 VHS domain is shown with solid bars to indicate α-helices. Residues shown to be critical for VHS domain–Ub binding are shaded in red, and other residues involved in, but not essential for, the interaction are shaded in blue. Identically conserved residues that are not directly involved in binding are shaded gray. Species abbreviations: Hs, Homo sapiens; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; and Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (B) Schematic of the domain organization of selected VHS domain-containing proteins. Of the sequences shown in (A), the domain structure of STAM2_Hs is like that of STAM1_Hs; Hrs_Dm like that of Hrs_Hs, GGA1_Hs, and GGA2_Hs like GGA3_Hs; and GGA2_Sc like GGA1_Sc. SH3, Src homology-3 domain; core, ESCRT-0 core GAT and coiled coil region responsible for heterodimerization; PSAP, PTAP, PSDP are ESCRT-I binding motifs; CB, clathrin binding; and GAE, γ-adaptin ear domain.