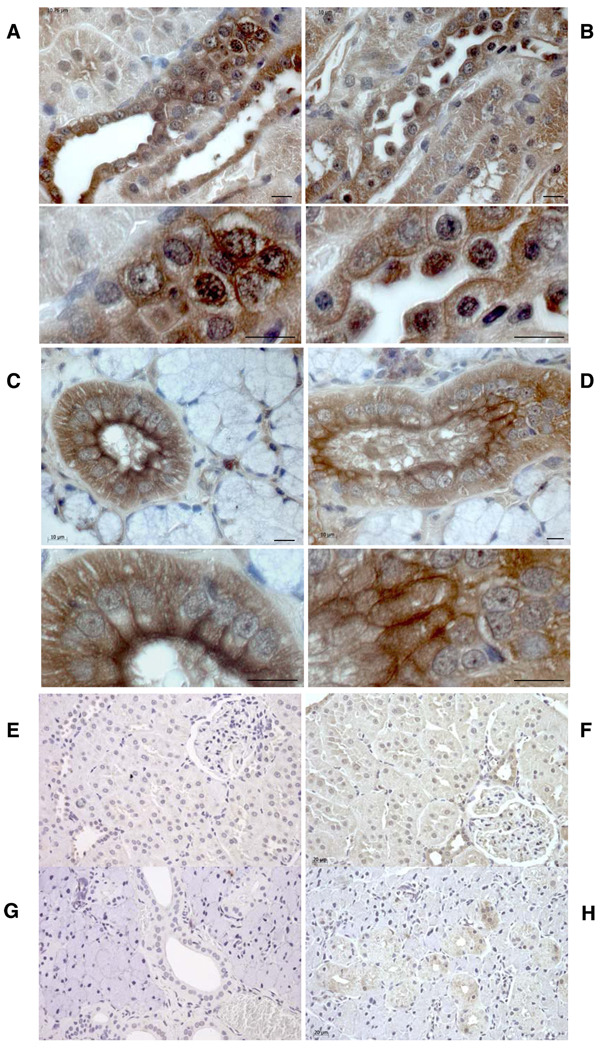
Fig. 5.
Immunohistochemistry analysis of NAVR/AVR protein. With an antibody raised against the NAVR/AVR common peptide sequence K592DELKDEE599, NAVR/AVR-positive immunostaining of renal epithelial plasma and nuclear membrane is detected in renal cortical collecting duct epithelial cells (A) and medullary thick ascending limb and collecting ducts (B). Corresponding high magnification reveals plasma and nuclear membrane staining. C and D: NAVR/AVR immunostaining is also detected in plasma membranes of salivary gland epithelial cells, with less nuclear membrane staining compared with renal epithelial cells. E–H: Negative controls for renal (E, F) and salivary gland (G, H) immunostaining done with preimmune serum and no anti-AVR/NAVR antibody (E, G) and done with 100× molar excess of AVR/NAVR common peptide sequence as competitor (F, H). NAVR/AVR-positive immunostaining, brown due to DAB chromogen; blue nuclei, Mayer’s hematoxylin counterstain. Bars: 10 µm (A–D), 40 µm (E–H).