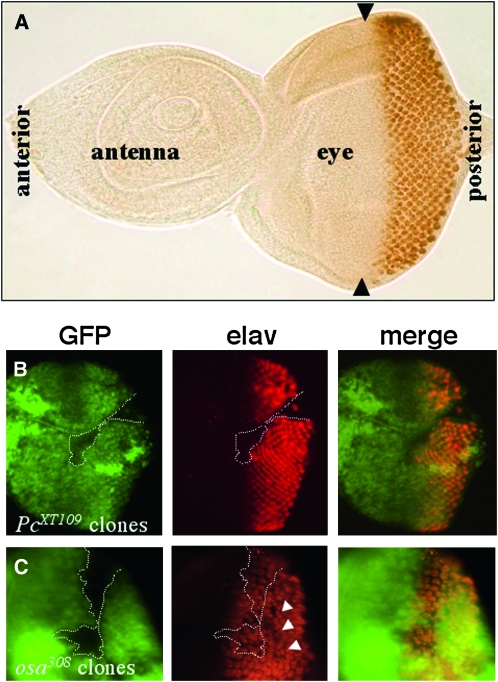
Figure 3.—
Loss of Polycomb and osa function disrupt eye development. (A) Wild-type eye-antennal imaginal disc labeled with anti-Elav. Differentiating photoreceptor cells (brown) are confined to the posterior half of the eye disc, behind the morphogenetic furrow (indicated by arrowheads). (B and C) Eye imaginal discs with mutant osa308 and PcXT109 cell clones were stained with anti-GFP to identify the position of the clones (absence of green GFP signal indicated by dotted lines) and anti-Elav (red) to mark differentiating photoreceptor cells. (B) No photoreceptor cells are specified within a large Pc clone. (C) A large osa clone disrupts the regular spacing of the photoreceptor clusters even outside the clone (arrowheads), indicating a cell-nonautonomous function.