Figure 2.
Phenotypes of nad9 5′ Termini in Different Arabidopsis Mutant Lines.
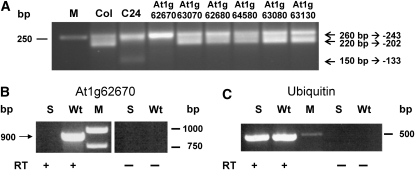
(A) Nad9 mRNA extremities were analyzed by CR-RT-PCR analysis as described in Methods. While the T-DNA insertions in At1g63070 (SALK 128068), At1g62680 (SALK 139736), At1g64580 (SALK 087235), At1g63080 (SALK 020638), and At1g63130 (SALK 020230) did not alter the 5′ end pattern of nad9 transcripts in comparison to Col wild type, an insertion in At1g62670 (SALK 146198) abolished the detection of the nad9 5′ ends at −202 as seen in the C24 wild type. In this mutant, the nad9 −133 5′ end is not detectable. CR-RT-PCR analysis of SALK 146198 was performed with three independent biological samples in at least three technical replicates. Lines with CR-RT-PCR product patterns identical to the wild type were investigated with single tests.
(B) RT-PCR analysis of SALK 146198 (S) mutant and Col wild type. An At1g62670 cDNA product of the expected size of 900 bp was amplified from wild-type RNA, while no such fragment is detectable in the mutant (RT +). No product is obtained without reverse transcriptase (RT −), demonstrating that the product derives from cDNA and not from DNA contaminations.
(C) The integrity and the use of equal amounts of the RNA and cDNA are indicated by the amplification of a 500-bp product from the ubiquitin 10 mRNA.