Figure 2.
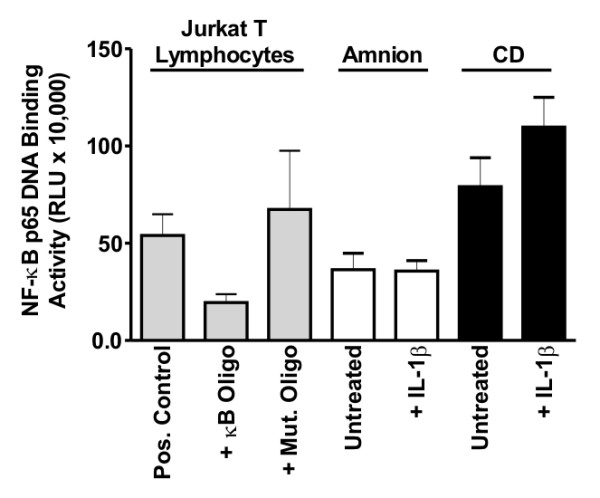
DNA binding of NF-κB p65 in fetal membrane explant cultures. Nuclear protein extracts from amnion (10 μg/well) and choriodecidua (6 μg/well) explants incubated in the absence or presence of 10 ng/ml of IL-1β for 2 h were analyzed for NF-κB p65 binding activity using an ELISA-based chemiluminescent assay (mean ± SD, N = 4 explants). Values from the luminometer are expressed as relative light units (RLU). Specificity controls were conducted using Jurkat T lymphocyte extracts incubated in the absence (pos. control) or presence of an excess of unbound oligonucleotides bearing either the consensus (κB oligo) or mutated (mut. oligo) NF-κB binding motif; similar results were obtained when amnion or choriodecidual lysates were incubated with these oligonucleotides (not shown). Relative to the untreated explants, explants stimulated with IL-1β did not show significant increases in p65 binding activity.
