Table 3. Insulin resistance significant DE genes.
| Symbol | Description | Direction | SAGAT PFER | FC PFER |
| FOSB* | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B | Up |
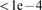
|
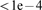
|
| ACTG2 | actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric | Down | 0.0007 | 0.0007 |
| FADS1* | fatty acid desaturase 1 | Down | 0.0022 | 0.0048 |
| PMP2 | peripheral myelin protein 2 | Down | 0.0034 | 0.0770 |
| ATP1A2 * |
ATPase,
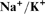 transporting, alpha 2
transporting, alpha 2
|
Down | 0.0040 | 0.1620 |
| CNN1 | calponin 1, basic, smooth muscle | Down | 0.0067 | 0.0114 |
| CSN1S1 | casein alpha s1 | Down | 0.0123 | 0.0004 |
| SELE* | selectin E (endothelial adhesion molecule 1) | Up | 0.0174 | 0.0006 |
| CASQ2 | calsequestrin 2 (cardiac muscle) | Down | 0.0176 | 0.0238 |
| FAM150B | family with sequence similarity 150, member B | Down | 0.0188 | 0.0006 |
| FASN * | fatty acid synthase | Down | 0.0231 | 0.0610 |
| FOS * | v-fos FBJ osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog | Up | 0.0242 | 0.0885 |
| SRGN | serglycin | Up | 0.0249 | 0.6952 |
| CILP | cartilage intermediate layer protein | Up | 0.0271 | 0.0420 |
| CXCR4 * | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | Up | 0.0311 | 0.6058 |
| PPBP* | pro-platelet basic protein (chemokine ligand 7) | Down | 0.0325 | 0.0355 |
| AADAC | arylacetamide deacetylase (esterase) | Up | 0.0374 | 0.0019 |
| ELOVL6 * | long chain fatty acid elongation | Down | 0.0425 | 0.0734 |
| IL6 * | interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) | Up | 0.1340 | 0.0120 |
Significance was determined by running the Rank Products (RP) algorithm on ranked lists of genes derived from Affymetrix, Agilent, and Illumina microarray data. Genes were ranked by both fold change and SAGAT before applying RP; the PFER (per family error rate) is displayed for both cases. Only those genes with a PFER of .05 or smaller (achieved using SAGAT or fold change) are considered significant. Genes in normal font were significant using both fold change and SAGAT, genes in bold were identified only with SAGAT, and IL6 was found only with the fold change metric.
*Literature evidence implicates gene with insulin resistance, diabetes, or fatty acid metabolism.
