Figure 2.
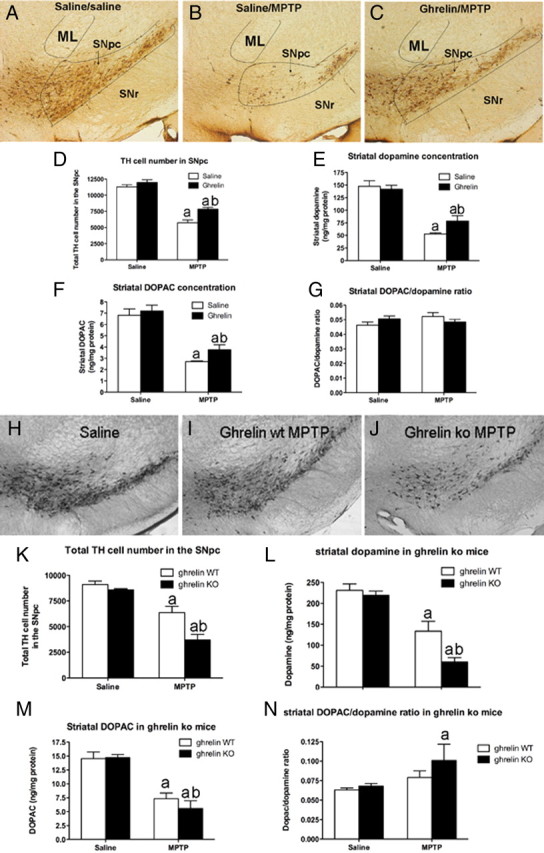
Ghrelin attenuates MPTP-induced nigrostriatal DA damage. A–C, Representative images showing MPTP-induced TH cell loss in the SNpc of saline/saline, saline/MPTP, or ghrelin/MPTP-treated mice. In each picture the SNpc, indicated by the black lines, is at the same approximate rostrocaudal extent. ML represents the medial lemniscus and SNr represents the substantia nigra reticulata. D, Unbiased stereological quantification of total TH cell number in the SNpc shows that ghrelin restricts MPTP-induced TH cell loss (n = 6). E, F, Ghrelin restricts dopamine loss (E) as well as DOPAC loss (F) in the striatum (n = 6). G, No difference in striatal DOPAC/dopamine ratio was observed (n = 6). aSignificant with respect to saline or ghrelin/saline-treated mice; bsignificantly increased compared with saline/MPTP-treated mice (p < 0.05). H–J, Lower-power images showing representative DA cell number in SNpc after saline (H, n = 10), MPTP to ghrelin wt (I, n = 8), or MPTP to ghrelin −/− mice (J, n = 9). Note the significant loss of DA neurons in ghrelin −/− mice treated with MPTP compared with ghrelin wt MPTP-treated mice. K, Stereological quantification shows that ghrelin −/− mice have significantly fewer surviving DA cells in the SNpc. L, Ghrelin −/− mice also exhibit reduced striatal DA content compared with wt after MPTP intoxication. M, Striatal DOPAC concentrations in ghrelin wt and ghrelin −/− mice did not differ. N, Striatal DOPAC/dopamine ratio was increased in ghrelin −/− mice but not ghrelin wt mice after MPTP. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aSignificant with respect to saline controls; bsignificant with respect to wt MPTP (p < 0.05).
