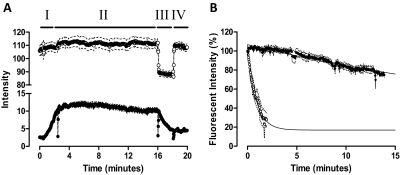
Fig. 8.
Brilliant Black BN (50 μM) enhances the dissociation rate of XAC-X-BY630 from the adenosine A1 receptor. A, real-time confocal imaging showing XAC-X-BY630 (●; 3 nM) association kinetics (I) followed by the dissociation kinetics in the absence (II) and presence (III) of Brilliant Black BN (50 μM). Fluid exchange was attained using a perfusion system. The intensity readout from the phase image (○; upper trace) clearly shows the rapid addition (III) and removal (IV) of Brilliant Black BN from the field of view. Data represents the mean intensity ± S.E.M. from the plasma membrane of 10 cells within a single experiment. B, the dissociation kinetics of 3 nM XAC-X-BY630 in the absence (●) and presence (○) of 50 μM Brilliant Black BN from CHO A1 cells at 37°C. Data are expressed as the percentage fluorescent intensity and represent the mean ± S.E.M. from four separate experiments in which each replicate reflects the fluorescent intensity from the plasma membrane of 10 cells. Confocal microscopy was performed on a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal microscope using a helium neon laser emitting at 633 nm and a long-pass emission filter at 650 nm.