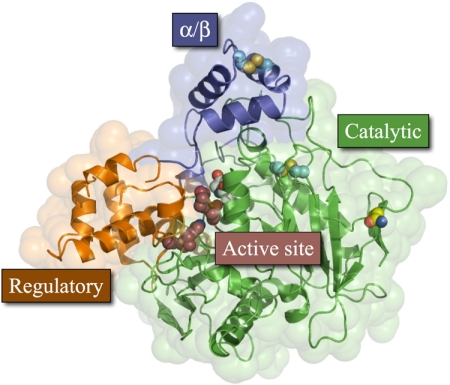
Fig. 2.
hCE1 monomer. Each protein monomer has three domains; the α/β domain (blue) forms the trimer interface and caps the active site; the regulatory region (orange) contains the secondary surface binding site (Z-site) and Glu354 of the catalytic triad; and the catalytic domain (green) contains the central β-sheet conserved in serine hydrolases and the two catalytic residues His468 and Ser221. There are two disulfide bonds (cyan), one in the α/β domain and the other in the catalytic domain, and one glycosylation site, at Asn79 (yellow).