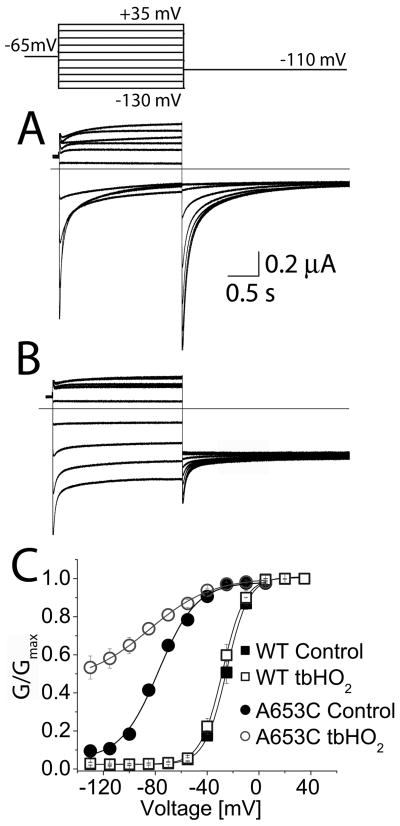
Fig. 5.
Oxidizing conditions alter gating of A653C hERG1 channels. (A and B) Current traces recorded from A653C channels before (A) and after (B) application of 2 mM tbHO2. Oxidized channels did not fully close at negative potentials. Inset above panel A shows voltage pulse protocol. (C) The voltage dependence of activation for WT and A653C channels before and after application of tbHO2. The G-V relationship for WT channels was not appreciably altered by oxidation. Control (■): V1/2 = −25.0 ± 0.3 mV, k = 8.4 ± 0.2 mV; after tbHO2 (□): V1/2 = −28.0 ± 0.2 mV, k = 8.5 ± 0.2 mV (n = 8). Oxidation of A653C channel currents caused a negative shift in V1/2 and an increase in the minimum value for G/Gmax. Control (●): V1/2 = −77.4 ± 1.5 mV, k = 14.7 ± 1.4 mV; after tbHO2 (○): V1/2 = −84.5 ± 2.5 mV, k = 24.1 ± 2.2 mV (n = 9).