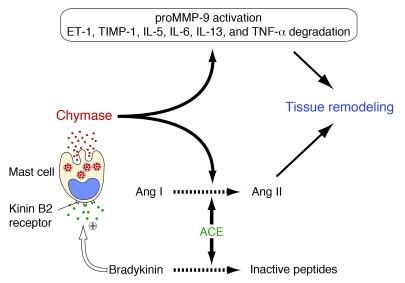
Figure 8. ACE-dependent bradykinin degradation limits baseline secretion of MC chymase in the LV.
Chronic inhibition of ACE reduces its direct effects on Ang I to Ang II conversion, but it increases bradykinin/B2 receptor–dependent chymase release from MCs, which counteracts the direct effect of ACE inhibition on Ang II formation through the chymase pathway of Ang II formation. In this scheme, we suggest that the effect of bradykinin on MC chymase release is direct; however, it is also possible that the bradykinin/B2 receptor mechanism indirectly causes chymase release. Chymase release also has a myriad of effects on factors that promote the inflammatory response and tissue remodeling. ET-1, endothelin-1; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor-1 of metalloproteinase.