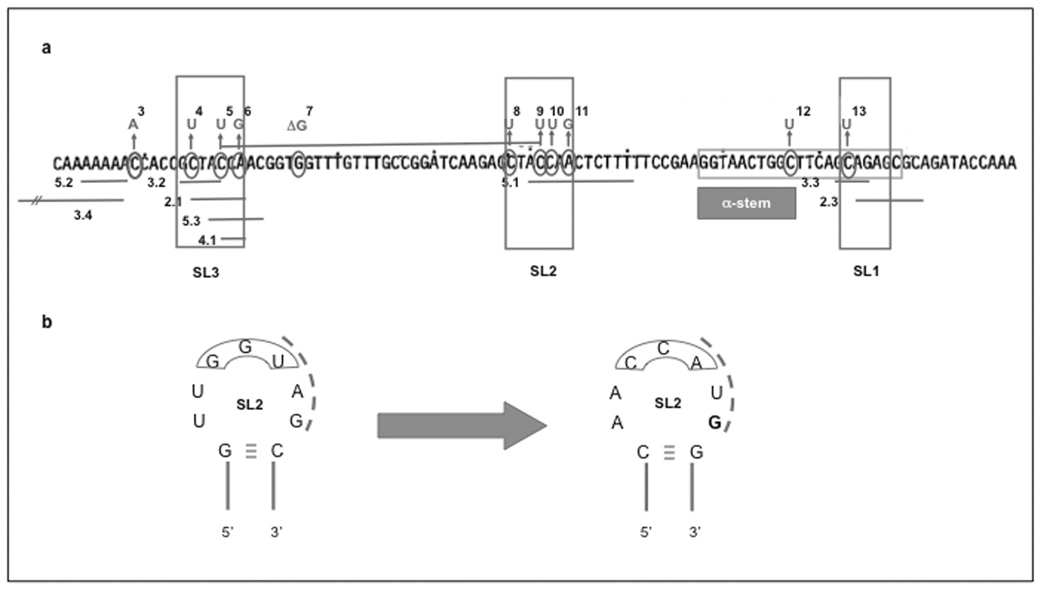
Fig. (6). Complex proprietary mutants.
a Deletion mutants in SL1, 2 and 3 [49, 50]. Deleted sections as reported in [50] (and patented [49]) are represented as lines below the sequence, with their identifiers next to them. For comparison, point mutants that increase copy number are also presented as numbers above the sequence. The legend to the numbers can be found in Table (2). b Inverted homology to tRNAs. Seven bases of SL2 (all but one G, in bold) were replaced by their complement bases, thereby inverting tRNA homologies without changing the complementarity between inhibitor and target RNA or any structural features of the stem-loop. A construct bearing the mutant ori and superoxide dismutase showed no signs of disregulation after induction of the recombinant protein in batch fermentation culture.