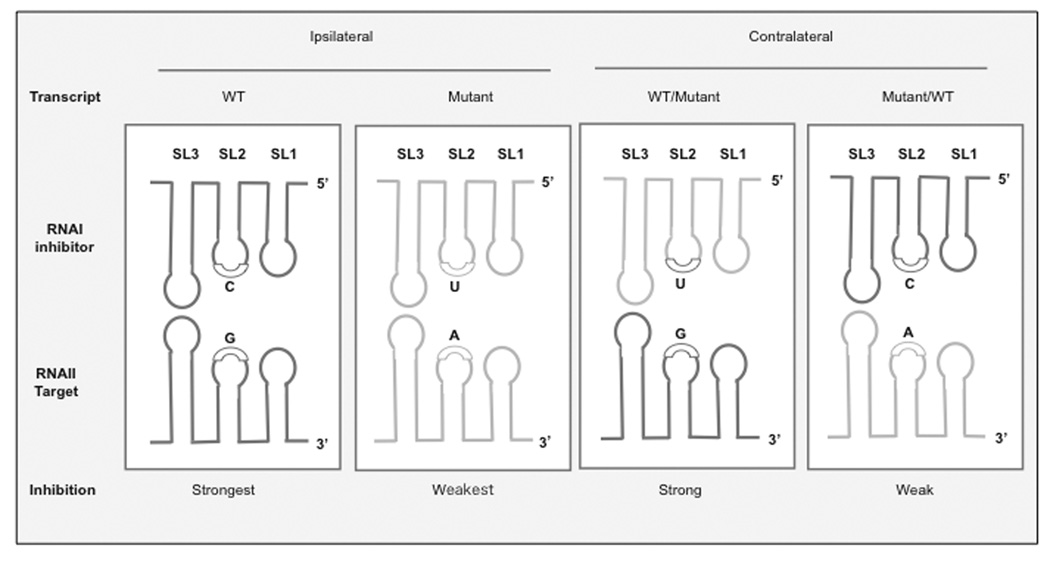
Fig. (7). Effect of mutations affecting SL1, 2 ,or 3 interactions on contralateral regulation.
A G→ A point mutation is presented as an example. If the mutant plasmid coexists with the wild-type plasmid, two inhibitor RNA I species are present. The corresponding contralateral interactions are: WT RNA I (encoding C) is opposite an A, a weak interaction, and mutant RNA I (encoding a U) opposite a G, a less-destabilizing interaction. This asymmetrical effect leads to the preferential elimination of the plasmid that is more efficiently repressed, the wild-type plasmid in this case.