Figure 5. Molecular basis for Pol γ sensitivity to ddNTP inhibition.
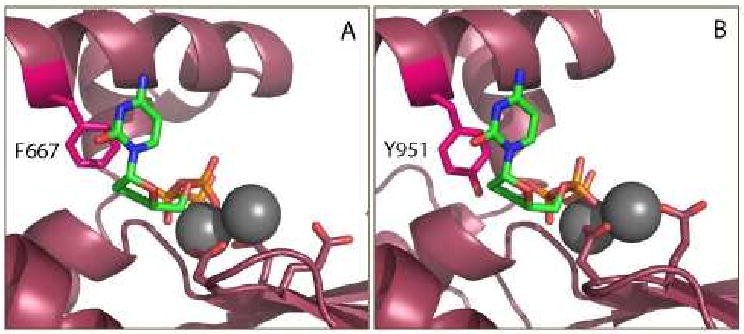
A) Pol I is resistant to dideoxynucleotide inhibition, which has been linked to the presence of a phenyalanine at position 667 on the O-helix, shown in fuschia. Image created from the ternary complex of the catalytic subunit ternary complex of Klentaq [120]. B) Molecular model of the Pol γ active site [112] demonstrates the phenolic hydroxyl group of Y951 mimicking the 3′-OH of a bound dNTP, allowing efficient incorporation of ddNTPs. ddCTP is shown bound to the Pol I and Pol γ active sites in green, with coordinated Mg2+ ions (gray), and catalytic residues shown in stick form.
