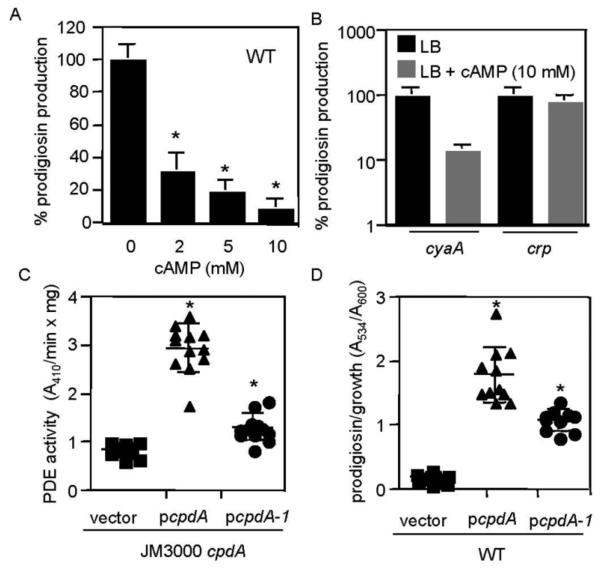
Fig. 2.
Exogenous cAMP inhibits prodigiosin production, whereas multicopy expression of a bona fide cAMP-PDE gene confers a hyperpigment phenotype. (A) Exogenous cAMP in LB medium elicits a dose-dependent reduction in prodigiosin production from the WT strain. Prodigiosin levels normalized by culture density are shown as a percentage of WT without exogenous cAMP. This experiment shows the average of 11-12 independent replicates per cAMP concentration from three experiments performed on different days. (B) Prodigiosin levels with respect to culture density in the presence or absence of cAMP (10 mM) in LB medium. Prodigiosin production by the cyaA, but not crp mutant is sensitive to exogenous cAMP. This experiment shows the average of 6 independent replicates per genotype; the experiment was performed two times on different days. (C) Phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity from crude lysates of a cpdA mutant of E. coli with an empty pBBR1-based vector, the vector expressing WT cpdA from E. coli (pcpdA), or a mutant version (pcpdA-1) using bis-pNPP as a substrate. The WT cpdA gene confers PDE activity, whereas the pcpdA-1 mutant confers an intermediate phenotype, indicating partial function. The data are from 10-12 independent replicates from two separate experiments performed on different days. Experiments were performed in LB medium. (D) Prodigiosin production by WT S. marcescens bearing an empty pBBR1-based vector, the vector expressing WT cpdA from the E. coli Plac promoter (pcpdA), or a partial-function mutant version (pcpdA-1). The cpdA gene confers a hyperpigment phenotype to the WT, and the pcpdA-1 mutant confers an intermediate phenotype. The data are from n≥10 independent replicates from two separate experiments performed on different days. Experiments were performed in LB medium. Asterisk = statistically significant difference from prodigiosin levels achieved without cAMP (p<0.05) by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post-test. Error bars = one standard deviation.