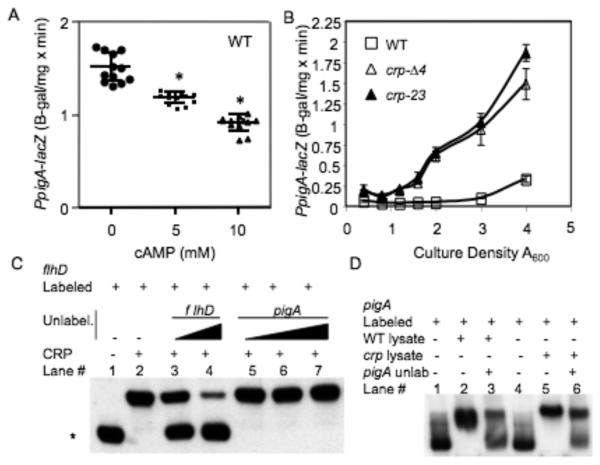
Fig. 3.
A chromosomal pigA-lacZ fusion is regulated by CRP and exogenous cAMP. (A) Exogenous cAMP in LB medium elicits a dose-dependent reduction in chromosomal pigA-lacZ ß-galactosidase activity at A600=5.5 in a WT background. This experiment shows the average of 12 independent replicates per cAMP concentration, performed on two different days. (B) ß-galactosidase activity as expressed from the chromosomal pigA promoter with respect to culture density in LB medium. This experiment shows the average of 3 independent replicates per genotype, the experiment was performed two times on different days with similar results. Experiments were performed in LB medium. (C) Competitive EMSA to determine the ability of unlabeled DNA to compete with His8-CRP-flhD interactions. Biotin-labeled flhD promoter DNA (1 ng) was incubated with His8-CRP at 0 ng (lane 1) or 50 ng (lanes 2-7) per reaction. Unlabeled promoter fragments of flhD (lanes 3-4) and pigA (lanes 5-7) were incubated in the specified binding reactions at 0 ng (lanes 1-2), 50 ng (lane 3), 200 ng (lanes 4 - 5), 400 ng (lane 6) or 600 ng (lane 7). The asterisk indicates the migration of unbound labeled-flhD promoter DNA, signifying successful competitive inhibition of His8-CRP-flhD promoter interactions (lanes 3-4). (D) EMSA analysis with crude lysates. Biotin-labeled pigA promoter DNA (2 ng, lanes 1-6) was incubated with crude lysates from WT (lanes 2-3, 10 μg of protein) or crp-23 cultures (lanes 5-6, 8 μg of protein). Lanes 1 and 4 have no protein added. Unlabeled pigA promoter DNA (1100 ng) was added (lanes 3 and 6) to compete for binding. Asterisk = statistically significant difference from prodigiosin levels achieved without cAMP (p<0.05) by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post-test. Error bars = one standard deviation.