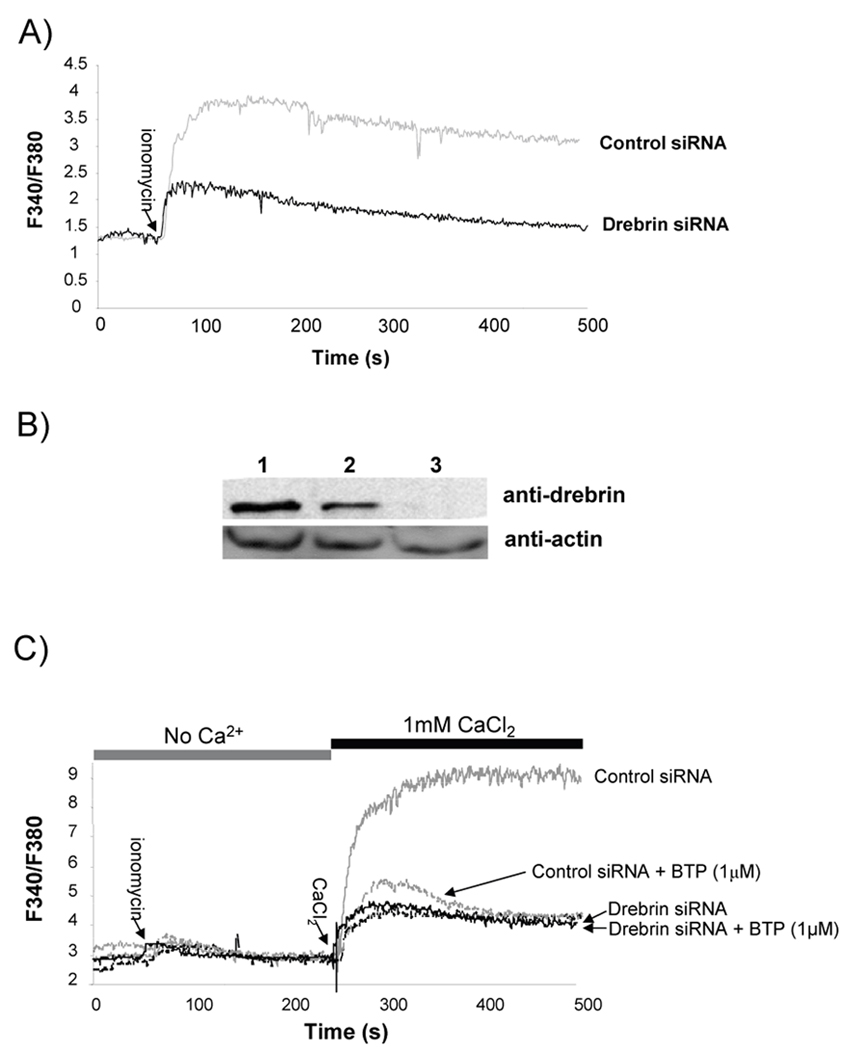
Figure 6. Loss of drebrin expression prevents extracellular calcium influx.
A) Jurkat T cells were transfected with either control siRNAs or drebrin-specific siRNAs and grown for 48 hours following transfection. Cells were then loaded with Fura-2AM and intracellular calcium concentration monitored in the presence of 1 mM extracellular Ca2+ before and after ionomycin treatment. One of 3 similar experiments. B) Representative drebrin knockdown 48 hours post-transfection in Jurkat T cells. Lane 1, Jurkat lysate no siRNA; Lane 2, Jurkat lysates from cells treated with control siRNA; or lane 3, Jurkat lysates from cells treated with drebrin-specific siRNA. One of 3 similar experiments. C) Jurkat T cells were transfected with either control or drebrin-specific siRNA. 48 hours post-transfection, cells were treated with DMSO or 1 µM BTP and then loaded with Fura-2AM. Intracellular calcium concentration was monitored following initial stimulation with ionomycin in the absence of extracellular calcium. After [Ca2+]i returned to baseline levels, 1 mM CaCl2 was added and calcium influx determined by monitoring the change in Fura-2 fluorescence. One of 3 similar experiments.