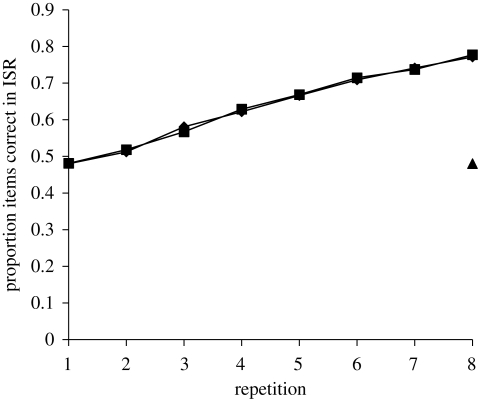
Figure 3.
A graph showing a positive repetition effect for each of two alternating and repeating lists. There was no overlap in item set between the lists. The triangle indicates performance, after learning has occurred, for a list derived from the first repeating list, in which alternating items (starting with the first) are maintained in the same positions as in the learned list, with the remaining items moving (cf. Cumming et al. 2003). Diamonds, repeating 1; squares, repeating 2; triangles, alternating items maintained from r1.