Table 3.
Subject and disease characteristics by starting imatinib dosage group
| Number of subjects | n ≤ 400 mg/day |
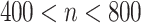
|
≥ 800 mg/day |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Males | 52 | 13 | 27 |
| Females | 48 | 13 | 16 |
| Continent | |||
| N. America | 83 | 25 | 37 |
| Europe | 10 | 0 | 6 |
| Asia | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Africa | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Oceania | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Unknown | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Primary tumor sitea | |||
| Upper-/mid-GI | 50 | 11 | 25 |
| Bowels | 36 | 11 | 17 |
| Other | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Unknown | 6 | 3 | 0 |
| Clinical trial participants | 21 | 9 | 17 |
| Mean age at diagnosis in years (SD) | 55.8 (12.2) | 50.3 (10.1) | 51.1 (10.3) |
| Minimum to maximum | 28.2–86.4 | 21.0–71.9 | 31.0–74.9 |
| Mean age at study start in years (SD) | 59.4 (12.2) | 54.9 (10.4) | 55.7 (10.4) |
| Minimum to maximum | 32.9–90.1 | 23.0–76.0 | 37.3–78.3 |
| Mean imatinib exposure in years (SD) | 4.6 (1.6) | 4.9 (1.7) | 4.9 (1.6) |
| Minimum to maximum | 0.9–7.1 | 1.8–7.3 | 1.1–6.8 |
aPrimary tumor sites were grouped post hoc as: upper-/mid-GI (esophagus, stomach, abdomen, omentum), bowel (small intestine, colon, rectum), other (liver, bladder, pancreas), and unknown.
