Fig. 1.
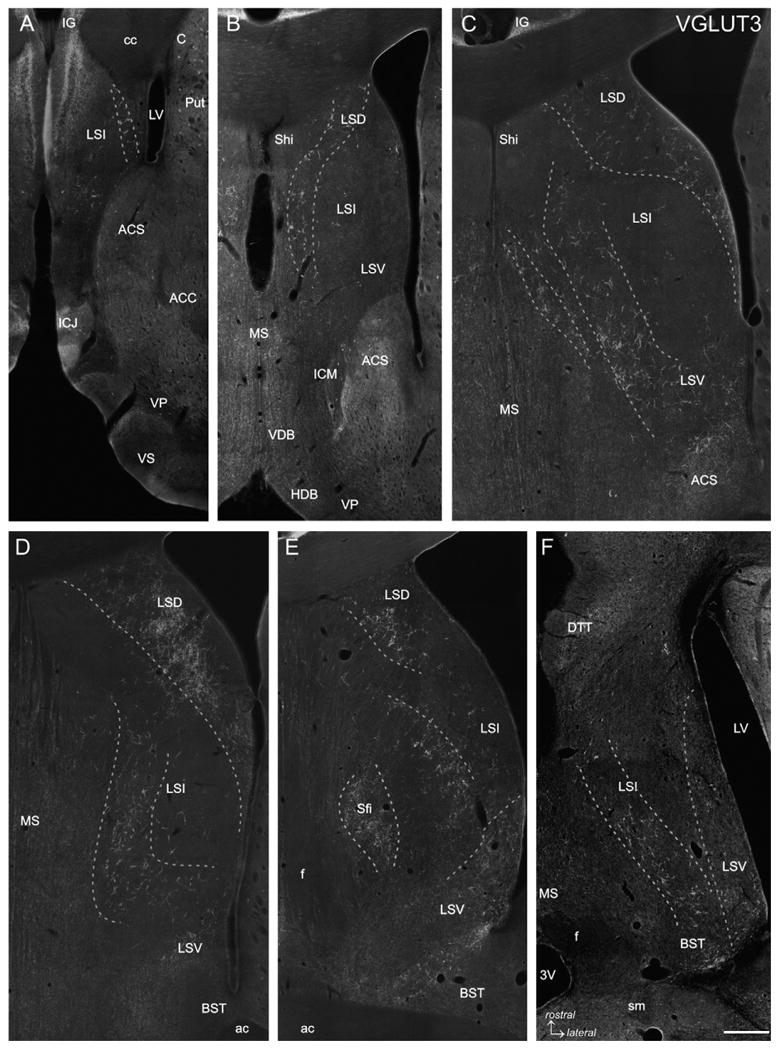
VGLUT3 immunofluorescence labeling. Five frontal sections covering the rostrocaudal extent of the lateral septum (Bregma +1.70 to −0.40 mm; A-E) and one horizontal section (Bregma −5.82 mm; Fig. 105 according to Paxinos and Watson, 1998; F) are represented. VGLUT3-ir baskets are arranged in more or less loosely arranged clusters forming oblique or curved bands which are indicated by dashed lines. In rostral and intermediate sections (A-C) VGLUT3-ir PBs occur very distinct even at low magnification, whereas in caudal sections (D and E) VGLUT3-ir PBs are less pronounced (LSD) or even absent (LSV) although a VGLUT3-ir fiber plexus is prominent. In the horizontal section (F) it is appreciable that the VGLUT3-ir PBs traversing the LSI form an oblique band from rostromedial to caudolateral, whereas the VGLUT3-ir fibers in the LSV are most prominent at the caudal level. The caudal tips of the LSV and LSI clusters merge with the VGLUT3-ir PBs in the BST (F). 3V: third ventricle; ac: anterior commissure; ACC: accumbens nucleus, core; ACS: accumbens nucleus, shell; C: caudate nucleus; cc: corpus callosum; BST: bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; DTT: dorsal tenia tecta; f: fornix; HDB: horizontal limb of the diagonal band; ICJ: island of Calleja; ICM: insula Calleja magna; IG: indusium griseum; LSD: dorsal nucleus of the lateral septum; LSI: intermediate nucleus of the lateral septum; LSV: ventral nucleus of the lateral septum; LV: lateral ventricle; MS: medial septal nucleus; Sfi: septofimbrial nucleus; sm: stria medullaris; VDB ventral limb of the diagonal band; VP: ventral pallidum; VS: ventral striatum. Scale bar (valid for A–F) = 500 μm.
