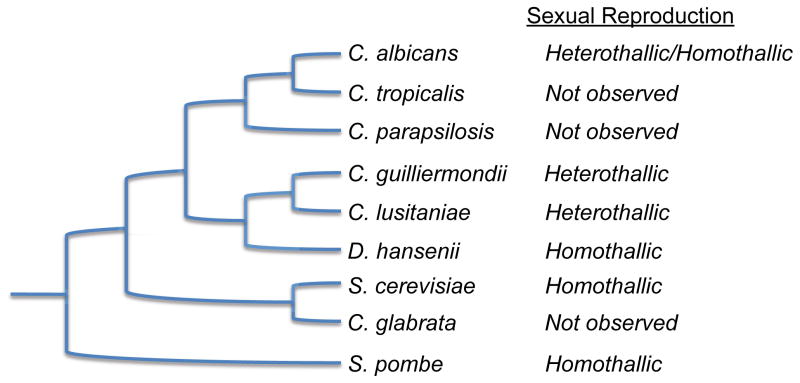
Figure 2. Phylogeny of Sequenced Candida Species.
Phylogenetic tree of the hemiascomycetes (S. cerevisiae and sequenced Candida species) as well as the related ascomycete, S. pombe. Heterothallic organisms are out-crossing species, whereas homothallic organisms are self-fertile. Note that C. albicans exhibits both homothallic and heterothallic modes of reproduction, but undergoes a parasexual cycle rather than a conventional meiosis. Most natural isolates of S. cerevisiae are homothallic although heterothallic isolates have also been described. Figure adapted from the Broad Institute (www.broadinstitute.org).