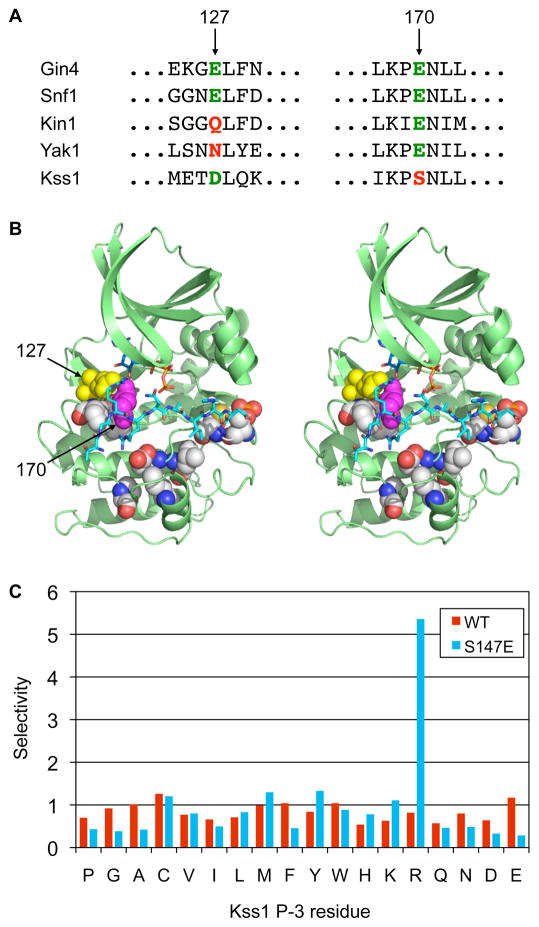
Fig. 4.
Comparison of kinase consensus phosphorylation site motifs to primary sequence reveals specificity-determining residues. (A) Sequence alignment of the regions surrounding residues 127 and 170 (human PKA numbering) in the catalytic domain of representative Snf1 family kinases (Gin4, Snf1, Kin1), and the CMGC kinases Yak1 and Kss1. The presence of an acidic residue at position 127 correlates with Arg selectivity at the P−3 position for the Snf1 family, but not the CMGC group. Conversely, a Glu residue at position 170 correlates with Arg selectivity for CMGC group kinases, but not for the Snf1 family. (B) Stereo view of the crystal structure of PKA with bound pseudosubstrate peptide (shown in cyan in stick representation; for clarity only the portion falling within the active site cleft is shown) highlighting predicted specificity determining residues (in sphere representation). Residues 127 and 170 are shown in yellow and magenta, respectively. The figure was generated using Pymol from the coordinates in PDB code 1ATP. (C) Kss1 mutagenesis. Mutation Kss1 Ser147 to Glu confers selectivity for Arg at P−3. The bar graph shows normalized spot intensities for the P−3 position taken from screens of the full peptide library (shown in Fig. S2).