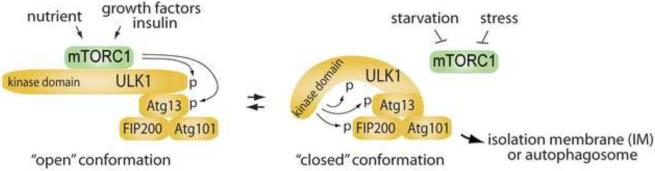
Figure 3.
(a) Two-state hypothesis for ULK1 conformation and activity. ULK1 interacts with Atg13, FIP200 and Atg101 through its C-terminal region [66,69,72,73,75]. Under high nutrient conditions, mTORC1 interacts with the ULK1 complex and phosphorylates ULK1 and Atg13 [66,71,72]. The phosphorylation may induce ULK1 to take an “open” conformation, an inactive form [69]. Under stress or starvation, mTORC1 is dissociated from the ULK1 complex. When mTORC1 could no longer phosphorylate ULK1 and Atg13 under the condition, ULK1 may take a “closed” conformation, an active form. In the closed-conformation state, the kinase domain of ULK1 may phosphorylate Atg13 and FIP200 and trigger the downstream events for autophagosome formation.