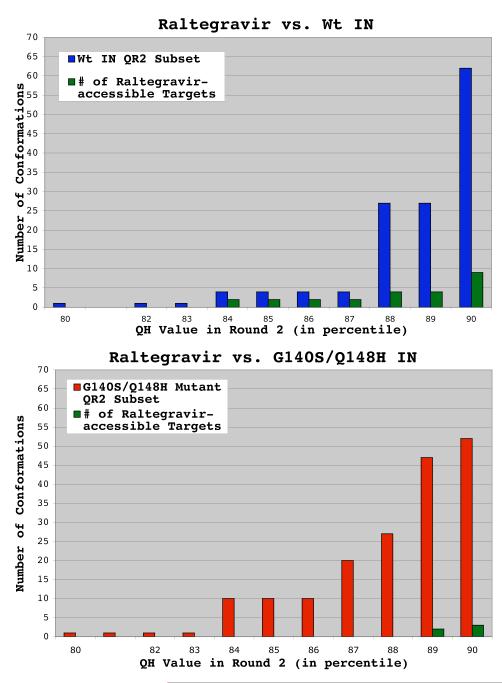
Fig. 7.
Wild type ensemble displayed a higher frequency of conformations against which raltegravir binds well. The QR Factorization tool in VMD was used to cluster and characterize snapshots harvested from MD simulations of the wild type and G140S/Q148H drug-resistant mutant of integrase. The results for wild type HIV integrase are presented in panel a, while the results for the G140S/Q148H mutant are presented in panel b. The number of conformations that passed through the structural diversity filter in the second round of QR factorization is plotted on the y-axis, while the QH value that extracted these results in the second round of filtering is plotted on the x-axis. When raltegravir was docked against the wild type ensemble of conformations extracted at a QH = 0.90, 9 of the 62 conformations produced binding modes in which raltegravir’s “three coplanar oxygen atoms” were between 1.7 and 2.3 Å from the magnesium ions. I.e., the w.t. ensemble contained 9 raltegravir-accessible targets. Using the same metrics, the G140S/Q148H mutant’s ensemble contained only 3 raltegravir-accessible targets.