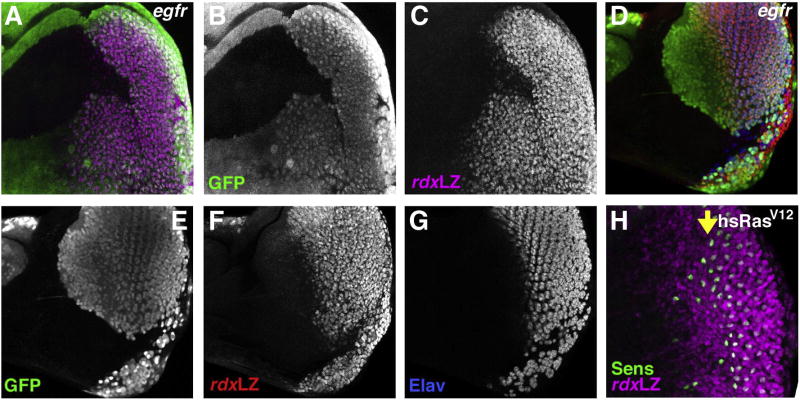
Fig. 4.
EGFR signaling and rdx expression. (A) Clone mutant for egfrf24 identified by the absence of GFP (green). Expression of rdxLacZ expression (magenta) is almost absent from the clones. A few scattered cells show some expression but this occurs throughout the clone and is not non-autonomous rescue near the clone boundaries. The GMRp35 transgene was used to suppress cell death in egfrf24 clones posterior to the furrow. (B) GFP channel. (C) rdxLacZ channel. (D) Clone mutant for egfrf24 identified by the absence of GFP (green). A few scattered cells that show some rdxLacZ expression (red) are also positive for the neural differentiation marker Elav (blue). Previous studies show that only R8 cells express Elav in the egfr mutant clones (Yang and Baker, 2001). The GMRp35 transgene was used to suppress cell death in egfrf24 clones posterior to the furrow. (E) GFP channel. (F) rdxLacZ channel. (G) Elav channel. (H) Effect of ectopic Ras activity in a hsRasV12 eye disc, 10 h after heat shock at 37 °C for 10 min. Sens labeling in green. Yellow arrow shows ommatidial column 0 in the morphogenetic furrow. Some ectopic R8 photoreceptors differentiate anterior to the furrow. rdxLacZ expression is induced anterior to the morphogenetic furrow (magenta).