Table 2.
Statistical methods used in the included papers to compare direct and proxy measures of behaviour
| Report | ni | nj | nk | Statistics used | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item-by-item comparisons: items treated as distinct | |||||
| Flocke, 2004[9] | 10 | 19 | 138 | ||
| Stange, 1998[19] | 79 | 32 | 138 | ||
| Ward, 1996[20] | 2 | 26 | 41 | Sensitivity = a/(a + c) | |
| Wilson, 1994[21] | 3 | 20 | 16 | ||
| Zuckerman, 1975[22] | 15 | 17 | 3 | ||
| Stange, 1998[19] | 79 | 32 | 138 | ||
| Ward, 1996[20] | 2 | 26 | 41 | ||
| Wilson, 1994[21] | 3 | 20 | 16 | Specificity = d/(b + d) | |
| Zuckerman, 1975[22] | 15 | 17 | 3 | ||
| Dresselhaus, 2000*[8] Gerbert, 1988[11] Pbert, 1999*[15] Rethans, 1987*[18] Wilson, 1994[21] |
7 4 15 24 3 |
8 3 9 1 20 |
20 63 12 25 16 |
Agreement: comparison of: (i) (a + b)/T, and (ii) (a + c)/T | Agreement was assessed by comparing the proportion of recommended behaviours performed as measured by the direct and proxy measures. Three reports performed hypothesis tests, using analysis of variance [8], Cochran's Q-test [15], and McNemar's test [18]. |
| Gerbert, 1988*[11] Pbert, 1999*[15] Stange, 1998[19] |
4 15 79 |
3 9 32 |
63 12 138 |
kappa = 2(ad - bc)/{(a + c)(c + d) + (b + d)(a + b)} | All three reports used kappa-statistics to summarise agreement; two reports [11,15] also used them for hypothesis testing. |
| Gerbert, 1988[11] | 4 | 3 | 63 | Disagreement = (i) c/T (ii) b/T (iii) (b + c)/T | Disagreement was assessed as the proportion of items recorded as performed by one measure but not by the other. |
| Item-by-item comparisons: items treated as interchangeable within categories of behaviour | |||||
| Luck, 2000[12] | NR | 8 | 20 | ||
| Page, 1980 [14] | 16-17 | 1 | 30 | Sensitivity = a/(a + c) | |
| Rethans, 1994[17] | 25-36 | 3 | 35 | ||
| Luck, 2000[12] Page, 1980[14] |
NR |
8 1 |
20 30 |
Specificity = d/(b + d) | |
| Gerbert, 1986[10] Page, 1980[14] |
20 16-17 |
3 1 |
63 30 |
Convergent validity = (a + d)/T | Convergent validity was assessed as the proportion of items showing agreement. |
| Comparisons of summary scores for each consultation: summary scores were the number (or proportion) of recommended items performed | |||||
| Luck, 2000*[12] | NR | 8 | 20 | Analysis of variance to compare means of scores on direct measure and proxy. | |
| Pbert, 1999*[15] | 15 | 9 | 12 | ||
| Summary score: | |||||
| Rethans, 1987*[18] | 24 | 1 | 25 | 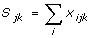 |
Paired t-tests to compare means of scores on direct measure and proxy. |
| Pbert, 1999*[15] | 15 | 9 | 12 | Pearson correlation of the scores on direct measure and proxy. | |
| Comparisons of summary scores for each clinician: summary scores were the number (or proportion) of recommended items performed | |||||
| O'Boyle, 2001[13] | 1 | NA | 120 | Comparison of means of scores on direct measure and proxy. | |
| Summary score: | |||||
| O'Boyle, 2001*[13] | 1 | NA | 120 | 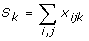 |
Pearson correlation of scores on direct measure and proxy. |
| Rethans, 1994*[17] | 25-36 | 3 | 25 | ||
| Comparisons of summary scores for each consultation: summary scores were weighted sums of the number of recommended items performed | |||||
| Peabody, 2000*[16] | 21 | 8 | 28 | Analysis of variance to compare means of scores on direct measure and proxy. | |
Summary score: 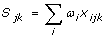
|
|||||
| Page, 1980*[14] | 16-17 | 1 | 30 | Pearson correlation of scores on direct measure and proxy. | |
a, b, c, d, T are defined in Table 1; i = item, j = consultation, k = physician, ni = average number of items per consultation, nj = average number of consultations per clinician; nk = average number of clinicians assessed; ωi = weight for ith item; xijk = 0 if item is not performed; xijk = 1 if item is performed;.
NR = Not reported; NA = Not applicable.
* This study used this method for hypothesis testing.
