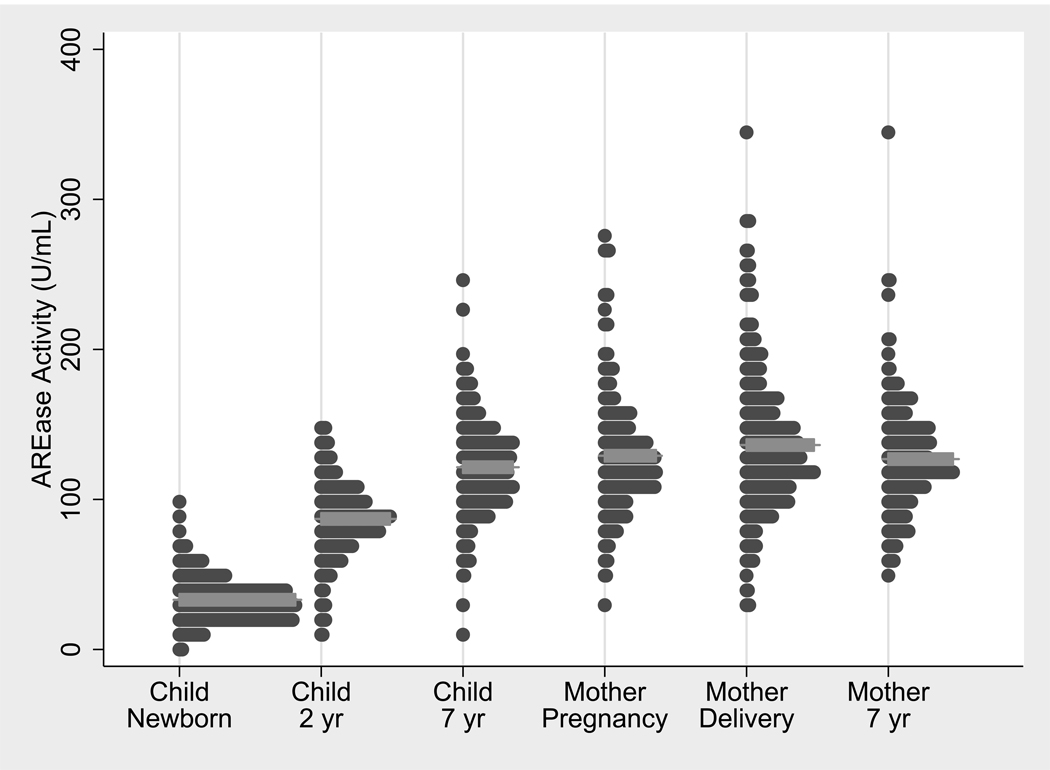
Figure 1.
The distribution of AREase in the CHAMACOS children at birth, age 2, and age seven and in their mothers during pregnancy (26 weeks gestation), at the time of delivery, and when their children were seven years old. Mean AREase activities as indicated by the grey horizontal bars, were 33.1, 89.2, 121.5 U/mL in children at birth, 2, and 7 years of age, respectively. In mothers, mean AREase activities were 129.1, 136.3, and 127.3 U/mL at pregnancy, delivery and seven years later, respectively. PON1 enzymatic activity was very low in newborns and continued to increase over time. At age seven, activities were still significantly lower than that of mothers at the same time point (p= 0.05). PON1 activities were elevated in mothers at the time of delivery (p<0.0005). This figure contains some of the children’s PON1 activity data (children at age two) modified from Huen et al. (2009a).