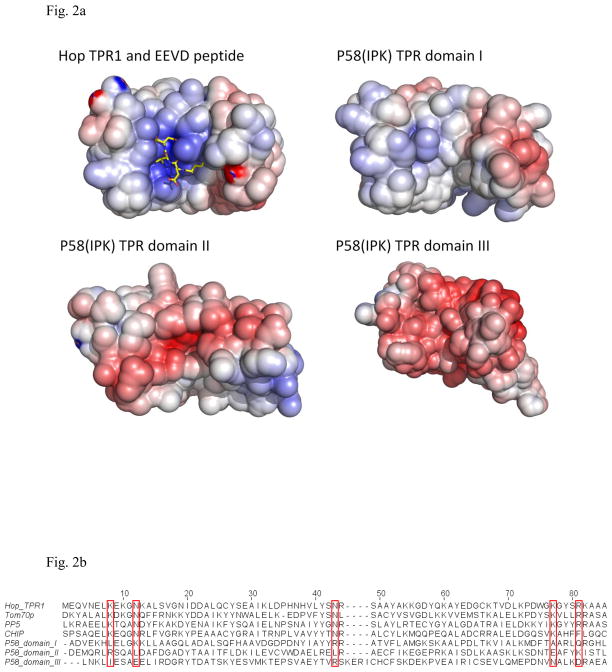
Fig. 2.
The individual domains within P58(IPK) TPR fragment compared with the TPR domains from other proteins.
a) The surface potential drawings for Hop TPR1 domain (PDB ID 1ELW), P58(IPK) TPR domain I, II and III (Blue for positively-charge regions; White for neutral regions; Red for negatively-charged regions). The groove of Hop TPR1 is positively charged which stabilizes the interaction between Hop TPR1 and EEVD motif of Hsp70 (in yellow stick representation). In contrast, P58(IPK) TPR fragment domain I is neutral in the groove while domain II and III are negatively-charged.
b) Alignment of Hop TPR1, Tom70p, PP5, CHIP and P58(IPK) TPR fragment domain I, II and III. The residues involved in EEVD motif binding are highlighted in the red boxes. These residues are highly conserved in Hop, Tom70p, PP5 and CHIP, but none of them is present in P58(IPK) TPR domain I, II or III.