Abstract
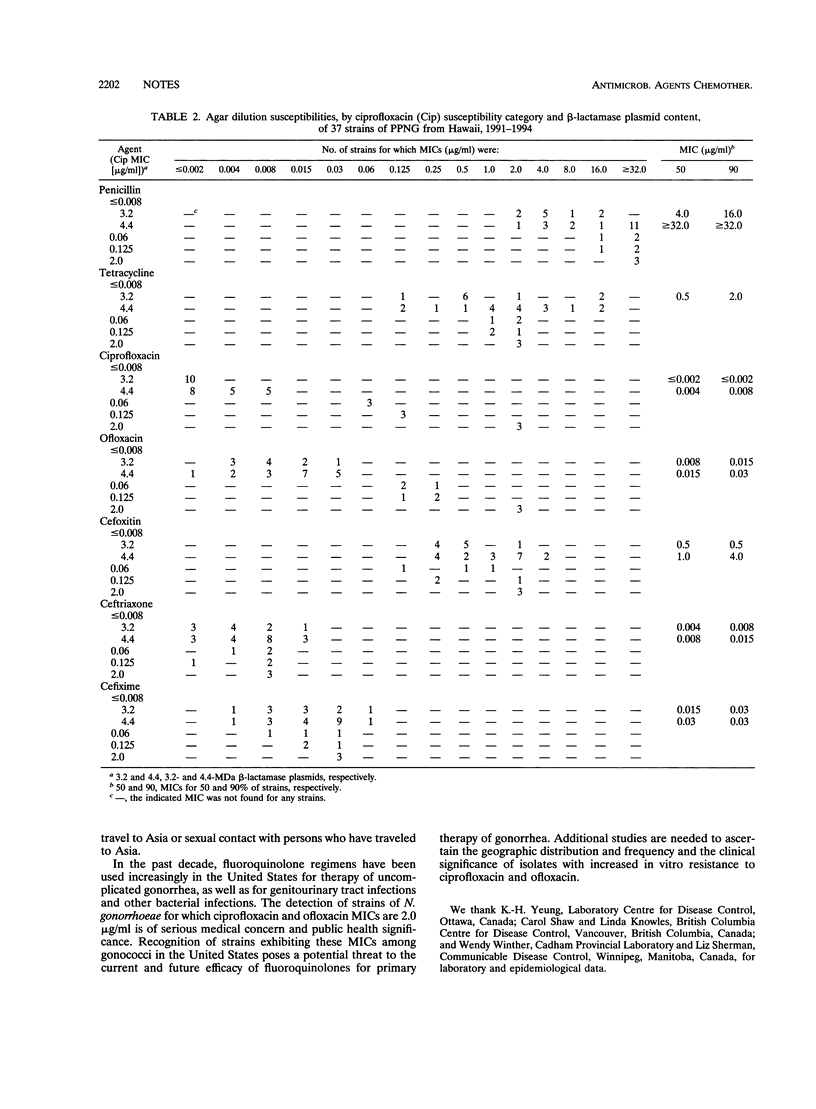
The susceptibilities of 37 penicillinase-producing strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (PPNG), isolated in Hawaii from December 1991 through January 1994, were determined to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin, fluoroquinolone agents currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as alternative regimens for the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea. Nine isolates (24.3%) exhibited decreased susceptibilities (MICs, > or = 0.06 microgram/ml) to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin MICs for three isolates (8.1%) were 2.0 micrograms/ml; these isolates belonged to the auxotype/serovar class Pro/IB-7 and possessed the 3.2-MDa beta-lactamase and the 24.5-MDa conjugative plasmids. Six strains for which ciprofloxacin MICs were 0.06 to 0.125 microgram/ml belonged to a variety of gonococcal phenotypes. Strains for which ciprofloxacin MICs were 2.0 micrograms/ml were isolated from persons who had traveled to, or were sexual contacts of persons who had recently traveled to, Southeast Asia. Persons infected with these isolates had been treated with ceftriaxone (250 mg intramuscularly, single dose); therefore, none of these cases were associated with clinical failure following the use of fluoroquinolone therapy. Further studies are needed to confirm the clinical and public health significance of increased in vitro resistance to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin in N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clendennen T. E., Echeverria P., Saengeur S., Kees E. S., Boslego J. W., Wignall F. S. Antibiotic susceptibility survey of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Thailand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1682–1687. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorwitz R. J., Nakashima A. K., Moran J. S., Knapp J. S. Sentinel surveillance for antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae--United States, 1988-1991. The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project Study Group. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1993 Aug 13;42(3):29–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Gavan T. L., Thornsberry C., Fuchs P. C., Gerlach E. H., Knapp J. S., Murray P., Washington J. A., 2nd Standardization of disk diffusion and agar dilution susceptibility tests for Neisseria gonorrhoeae: interpretive criteria and quality control guidelines for ceftriaxone, penicillin, spectinomycin, and tetracycline. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2758–2766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2758-2766.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Tam M. R., Nowinski R. C., Holmes K. K., Sandström E. G. Serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with use of monoclonal antibodies to gonococcal outer membrane protein I. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):44–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Johnson S. R., Biddle J. W., Roberts M. C. High-level tetracycline resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is result of acquisition of streptococcal tetM determinant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):664–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam S. D., Lavin B. S., Stone J. R., Oldfield E. C., 3rd, Hooper D. G. Evaluation of the standardized disk diffusion and agar dilution antibiotic susceptibility test methods by using strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae from the United States and Southeast Asia. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):974–980. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.974-980.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Ploscowe V. B., Weiss J. A., Young F. E. Rapid method for auxotyping multiple strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.244-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapsall J. W., Shultz T. R., Lovett R., Munro R. Failure of 500 mg ciprofloxacin therapy in male urethral gonorrhoea. Med J Aust. 1992 Jan 20;156(2):143–143. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1992.tb126457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


