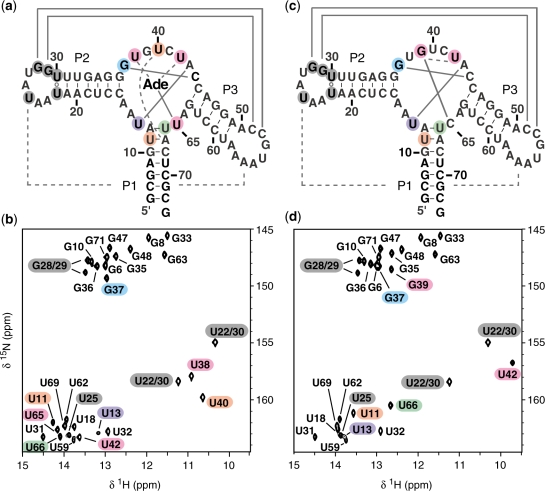
Figure 3.
Sequence and secondary structure of the wild-type (a) and U65C mutant (c) of the B. subtilis pbuE A-riboswitch aptamer. Below, the imino-optimized 2D 1H–15N HSQC spectra (20) of (b) the 15N-labeled wild-type aptamer with unlabeled adenine and (d) the 15N-labeled U65C mutant aptamer. The crosspeaks are annotated by residue types and numbers. Residues in loops L2 and L3 that yield a detectable imino signal in the HSQC spectra are shaded in dark grey, whereas those from the core are shaded in color as in Figure 4. The imino NMR data in (b) and (d) confirm the secondary structures in (a) and (c); canonical (WC/WC G–C and A–U) and non-canonical base pairs are connected by solid lines and open circles, respectively. The imino NMR data also provide evidence for tertiary interactions; canonical and non-canonical base pairs are shown in (a) and (c) by full and dashed lines, respectively. Spectra were recorded on a 600 MHz NMR spectrometer at 288 K.