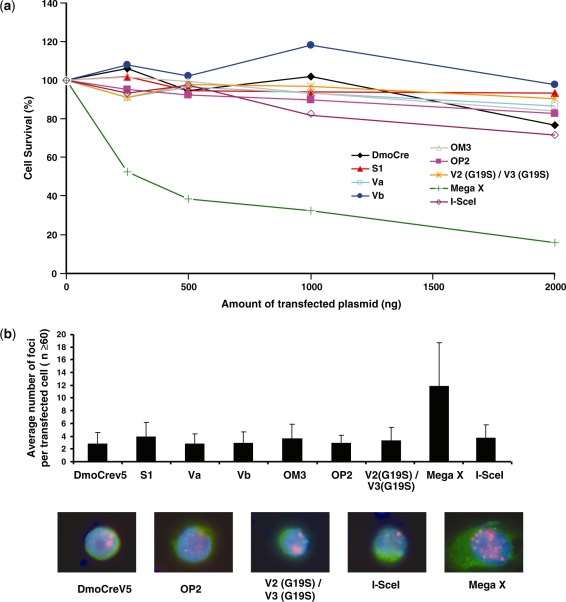
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the potential toxicity of the DmoCre meganucleases. (a) Toxicity of the DmoCre engineered meganucleases, as monitored by a cell survival assay. Increasing amounts of meganuclease expression vector and a constant amount of plasmid encoding GFP were used to cotransfect CHO-K1 cells. Cell survival is expressed as a percentage of cells expressing GFP 6 days after transfection as described in the ‘Materials and methods’ section. (b) The potential genotoxicity of the engineered DmoCre meganucleases was monitored by visualizing the formation of γ-H2AX foci at DNA double-strand breaks. CHO-K1 cells were transfected with 1 µg of a plasmid coding for different meganucleases carrying a C-terminal HA epitope. For each condition, the average number of γ-H2AX foci per transfected cell (HA positive) was determined. Pictures below are representative images of cells transfected with the DmoCreV5, OP2, V2 (G19S)/V3 (G19S), I-SceI and Mega X meganucleases: Green, HA labeling; red, γ-H2AX foci and blue, DAPI staining. The inactive V2 (G19S)/V3 (G19S) I-CreI heterodimer is shown as a control for non-toxicity, while Mega X is a meganuclease derived from I-CreI with relaxed specificity.