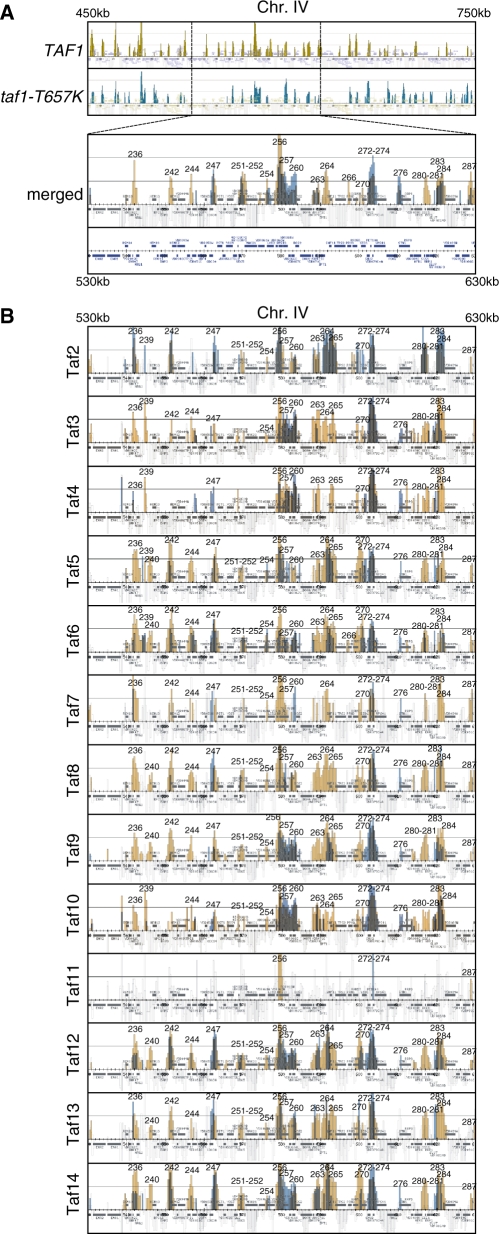
Figure 4.
Effects of the taf1-T657K mutation on the localization of Tafs on chromosomes III, IV and V. (A) Comparison of Taf1 localization in wild-type (top panel; significant occupancy is indicated by orange vertical bars) and taf1-T657K (second panel; significant occupancy is indicated by blue vertical bars) strains by combining two images into one (bottom panel, denoted as ‘merged’). Note that the region from 450 000 to 750 000 of chromosome IV is shown in the top two panels, whereas only a part of this region (from 530 000 to 630 000) is selectively shown as an enlarged image in the bottom ‘merged’ panel. The strains YTK2741 and YTK3780 expressing HA-tagged Taf1 and Taf1-T657K, respectively, were cultured and cross-linked as described in Figure 1A. The cross-linked chromatin was prepared and precipitated with anti-HA monoclonal antibody, and then analyzed by GeneChip as described in Figure 1A. The numbers above the occupancy signals correspond to those in Supplementary Table S3. (B) Comparison of the localization of the Tafs (i.e. Taf2-Taf14 as denoted at the left of each panel) in wild-type (orange bars) and taf1-T657K (blue bars) strains by generating merged images of the same region (from 530 000 to 630 000) of chromosome IV as described for Taf1 in A. Each pair of strains expressing one of the PK-tagged TAF genes as well as either HA-tagged TAF1 or taf1-T657K, which is abbreviated as [PK-tagged]TAFX (strain #[HA-tagged TAF1]/strain #[HA-tagged taf1-T657K]), i.e. TAF2 (YTK6818/YTK6845), TAF3 (YTK6819/YTK6846), TAF4 (YTK6820/YTK6847), TAF5 (YTK6821/YTK6848), TAF6 (YTK6822/YTK6849), TAF7 (YTK6823/YTK6850), TAF8 (YTK6824/YTK6851), TAF9 (YTK6825/YTK6852), TAF10 (YTK6826/YTK6853), TAF11 (YTK6827/YTK6854), TAF12 (YTK6828/YTK6855), TAF13 (YTK6829/YTK6856) or TAF14 (YTK6830/YTK6857), was cultured and cross-linked as described in (A). The cross-linked chromatin was prepared and precipitated with anti-PK monoclonal antibody, and then analyzed by GeneChip as described in (A). The complete data sets including Gcn5, NC2, pol II and other GTFs are represented in Supplementary Figures S8–10.