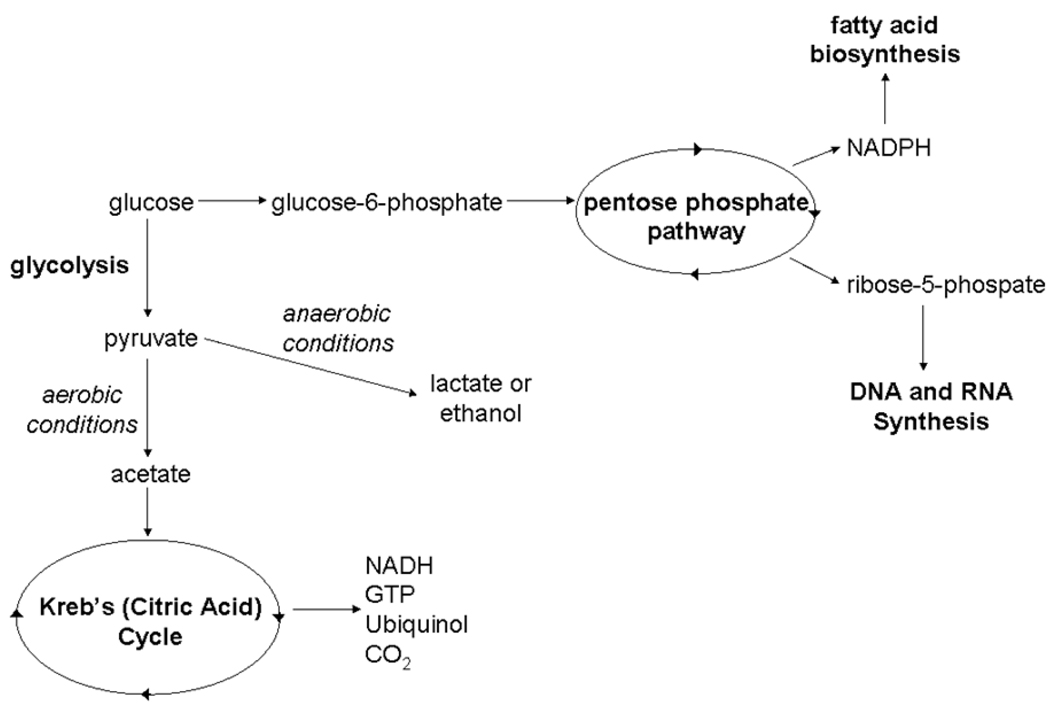
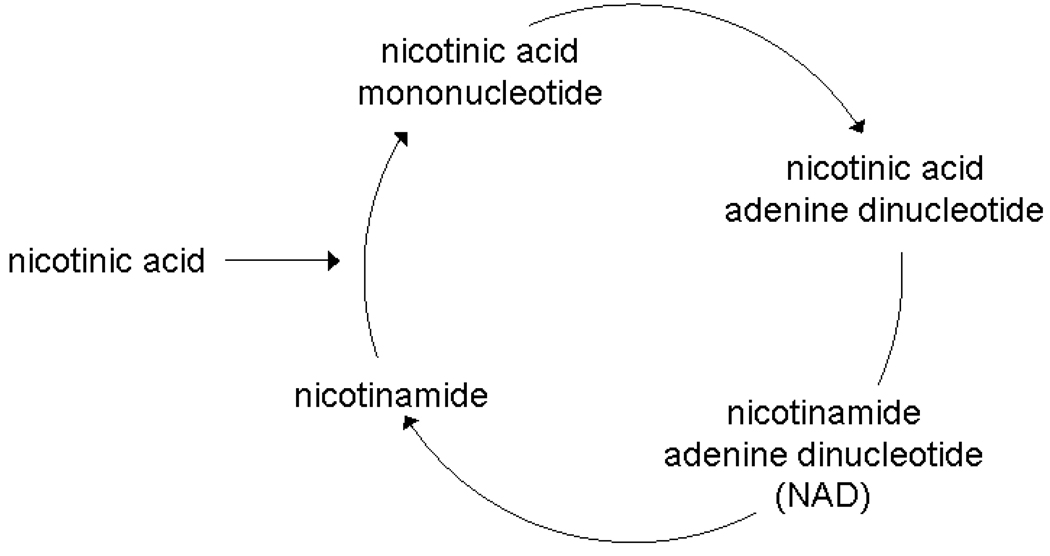
Figure 1.
Metabolic fates for glucose and nicotinic acid in yeast. Figure 1a:. A partial, simplified view of glucose metabolism in yeast. Glucose can be broken down into most major components of a cell and even given off as carbon dioxide. Ubiquitously labeled 14C-glucose will label most metabolites in these pathways. Major metabolite pathways are abbreviated and in bold. Figure 1b: Nicotinic acid metabolism in yeast is limited to four metabolites. 14C-nicotinic acid will only label these metabolites creating a very simple AMS trace.